python实现数字华容道
制作Python数字华容道(可选择关卡),供大家参考,具体内容如下
由于比赛需要,我这边制作了一份数字华容道,内含有3,4,5阶的数字华容道,开头在壳窗口内选择,运用了随机数模块(random)和图形化用户界面(tkinter)
下面是程序完整代码
# coding:utf-8 #'''#============================================================作者:@Qss2021年3月20日起草2021年3月21日完工2021年3月23日一次优化完成2021年3月31日完成二次优化(关卡设计)二次优化待解决漏洞:设计关卡后窗口不能自动显示,需手动切换2021年4月1日三次优化完成,成功解决二次优化bug#============================================================'''from random import * #导入随机数模块from tkinter import * #导入图形化用户界面模块step_number = 0 #设置步数的变量,初始值为0difficulty = int(input(’请输入数字华容道列数(3/4/5):’))def Button_Click_1(x,y): #按钮点击事件函数'''声明空白按钮行列号和步数的变量为全局变量'''global row_of_space global col_of_space global step_number'''判断判断点击按钮旁是否为空白按钮,是则交换位置'''if abs(x-row_of_space) + abs(y-col_of_space) == 1: step_number += 1 #将步数赋值 label_step_number[’text’] = ’步数:’ + str(step_number) #将步数变量导入label控件 '''交换按钮位置''' buttons[row_of_space,col_of_space][’text’] = buttons[x,y][’text’] buttons[x,y][’text’] = ’ ’ row_of_space = xcol_of_space = y n = 0 for row in range(3):for col in range(3): '''对比所有按钮序列是否正确,不正确则跳出函数''' if buttons[row,col][’text’] != numbers[n]: return n += 1 '''所有按钮判断完毕赢得游戏胜利''' label_welcomes[’text’] = ’你赢了’def Button_Click_2(x,y): #按钮点击事件函数'''声明空白按钮行列号和步数的变量为全局变量'''global row_of_space global col_of_space global step_number'''判断判断点击按钮旁是否为空白按钮,是则交换位置'''if abs(x-row_of_space) + abs(y-col_of_space) == 1: step_number += 1 #将步数赋值 label_step_number[’text’] = ’步数:’ + str(step_number) #将步数变量导入label控件 '''交换按钮位置''' buttons[row_of_space,col_of_space][’text’] = buttons[x,y][’text’] buttons[x,y][’text’] = ’ ’ row_of_space = xcol_of_space = y n = 0 for row in range(4):for col in range(4): '''对比所有按钮序列是否正确,不正确则跳出函数''' if buttons[row,col][’text’] != numbers[n]: return n += 1 '''所有按钮判断完毕赢得游戏胜利''' label_welcomes[’text’] = ’你赢了’def Button_Click_3(x,y): #按钮点击事件函数'''声明空白按钮行列号和步数的变量为全局变量'''global row_of_space global col_of_space global step_number'''判断判断点击按钮旁是否为空白按钮,是则交换位置'''if abs(x-row_of_space) + abs(y-col_of_space) == 1: step_number += 1 #将步数赋值 label_step_number[’text’] = ’步数:’ + str(step_number) #将步数变量导入label控件 '''交换按钮位置''' buttons[row_of_space,col_of_space][’text’] = buttons[x,y][’text’] buttons[x,y][’text’] = ’ ’ row_of_space = xcol_of_space = y n = 0 for row in range(5):for col in range(5): '''对比所有按钮序列是否正确,不正确则跳出函数''' if buttons[row,col][’text’] != numbers[n]: return n += 1 '''所有按钮判断完毕赢得游戏胜利''' label_welcomes[’text’] = ’你赢了’'''创建华容道游戏窗口'''root = Tk() #创建图形化用户界面实例root.title(’数字华容道’) #设置窗口标题root.geometry('400x400') #将窗口大小设为高400宽400root.configure(bg = ’black’) #将窗口背景设为黑色root.resizable(width = False,height = False) #设置窗口为不可拉伸'''设置欢迎语的label控件'''label_welcomes = Label(root,text = ’欢迎来到数字华容道’,bg = ’black’,fg = ’red’,font = ('Arial',13)) #设置label控件的属性label_welcomes.place(x = 20,y = 10,width = 250,height = 40) #设置label控件位置'''设置显示操作方式的label控件'''label_operation = Label(root,text = ’单击数字’,bg = ’black’,fg = ’white’,font = ('Arial',10))label_operation.place(x = 3,y = 40,width = 50,height = 30)label_operation_2 = Label(root,text = ’移动方块’,bg = ’black’,fg = ’white’,font = ('Arial',10))label_operation_2.place(x = 3,y = 60,width = 50,height = 30)'''设置显示步数的label控件'''label_step_number = Label(root,text = ’步数:’ + str(step_number),bg = ’black’,fg = ’yellow’,font = ('Arial',10))label_step_number.place(x = 3,y = 20,width = 50,height = 30)if difficulty == 3: root.attributes('-topmost', True) row_of_space = 0 #存放空白按钮的行号 col_of_space = 0 #存放空白按钮的列号 buttons = {} #存放数字按钮的数组 numbers = [’1’,’2’,’3’,’4’,’5’,’6’,’7’,’8’,’ ’] #所有数字文本的列表 shuffle(numbers) #打乱数字列表中的数字顺序 '''制造数字华容道方阵''' for row in range(3): for col in range(3): '''创建数字按钮,并将行列号传入该按钮的点击事件函数''' button = Button(root,command = lambda x = row,y = col:Button_Click_1(x,y),bg = ’black’,fg = ’green’,font = ('Arial',35)) buttons[row,col] = button #将按钮导入数组 button[’text’] = numbers.pop() #设置按钮上的文本 button.place(x = 60 + col * 60,y = 60 + row * 60,width = 50,height = 50) #设置数字按钮大小 if button[’text’] == ’ ’:#判断是否为空白按钮,如果是,则记录到空白按钮行列号变量row_of_space = rowcol_of_space = col numbers = [’1’,’2’,’3’,’4’,’5’,’6’,’7’,’8’,’ ’] #还原数字列表 root.mainloop() #显示窗口elif difficulty == 4: root.attributes('-topmost', True) row_of_space = 0 #存放空白按钮的行号 col_of_space = 0 #存放空白按钮的列号 buttons = {} #存放数字按钮的数组 numbers = [’1’,’2’,’3’,’4’,’5’,’6’,’7’,’8’,’9’,’10’,’11’,’12’,’13’,’14’,’15’,’ ’] #所有数字文本的列表 shuffle(numbers) #打乱数字列表中的数字顺序 '''制造数字华容道方阵''' for row in range(4): for col in range(4): '''创建数字按钮,并将行列号传入该按钮的点击事件函数''' button = Button(root,command = lambda x = row,y = col:Button_Click_2(x,y),bg = ’black’,fg = ’green’,font = ('Arial',35)) buttons[row,col] = button #将按钮导入数组 button[’text’] = numbers.pop() #设置按钮上的文本 button.place(x = 60 + col * 60,y = 60 + row * 60,width = 50,height = 50) #设置数字按钮大小 if button[’text’] == ’ ’:#判断是否为空白按钮,如果是,则记录到空白按钮行列号变量row_of_space = rowcol_of_space = col numbers = [’1’,’2’,’3’,’4’,’5’,’6’,’7’,’8’,’9’,’10’,’11’,’12’,’13’,’14’,’15’,’ ’] #还原数字列表 root.mainloop() #显示窗口elif difficulty == 5: root.attributes('-topmost', True) row_of_space = 0 #存放空白按钮的行号 col_of_space = 0 #存放空白按钮的列号 buttons = {} #存放数字按钮的数组 numbers = [’1’,’2’,’3’,’4’,’5’,’6’,’7’,’8’,’9’,’10’,’11’,’12’,’13’,’14’,’15’,’16’,’17’,’18’,’19’,’20’,’21’,’22’,’23’,’24’,’ ’] #所有数字文本的列表 shuffle(numbers) #打乱数字列表中的数字顺序 for row in range(5): for col in range(5): '''创建数字按钮,并将行列号传入该按钮的点击事件函数''' button = Button(root,command = lambda x = row,y = col:Button_Click_3(x,y),bg = ’black’,fg = ’green’,font = ('Arial',35)) buttons[row,col] = button #将按钮导入数组 button[’text’] = numbers.pop() #设置按钮上的文本 button.place(x = 60 + col * 60,y = 60 + row * 60,width = 50,height = 50) #设置数字按钮大小 if button[’text’] == ’ ’:#判断是否为空白按钮,如果是,则记录到空白按钮行列号变量row_of_space = rowcol_of_space = col numbers = [’1’,’2’,’3’,’4’,’5’,’6’,’7’,’8’,’9’,’10’,’11’,’12’,’13’,’14’,’15’,’16’,’17’,’18’,’19’,’20’,’21’,’22’,’23’,’24’,’ ’] #还原数字列表 root.mainloop() #显示窗口else: print(’未完成此类关卡’)
下面是程序运行结果
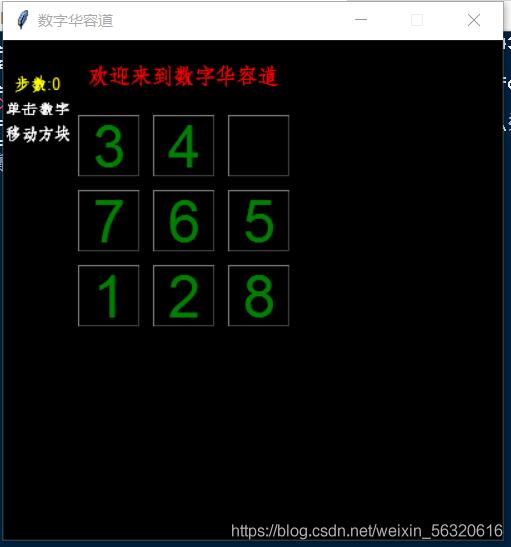
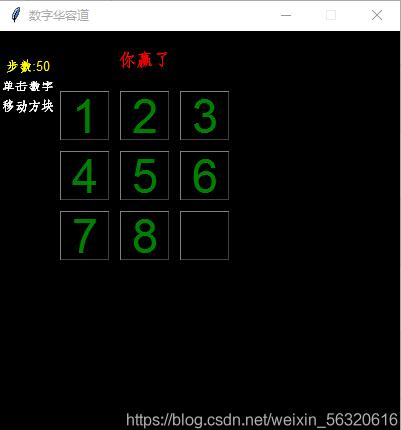
三阶华容道加胜利
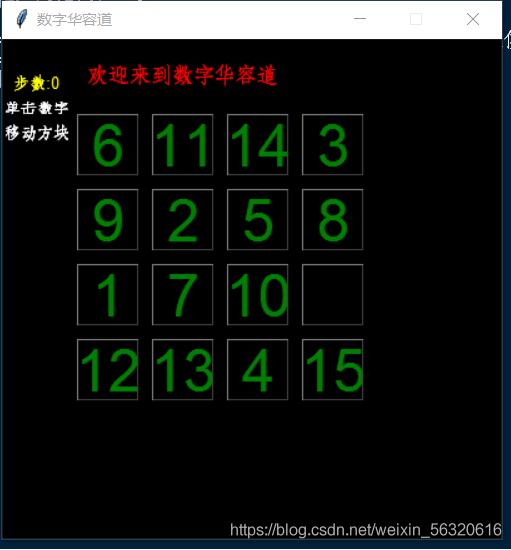
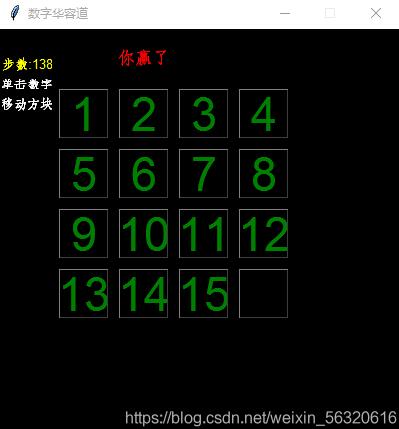
四阶华容道加胜利
五阶就不传了,都一样
接下来说一下代码原理
首先看下这一段
def Button_Click_1(x,y): #按钮点击事件函数'''声明空白按钮行列号和步数的变量为全局变量'''global row_of_space global col_of_space global step_number'''判断判断点击按钮旁是否为空白按钮,是则交换位置'''if abs(x-row_of_space) + abs(y-col_of_space) == 1: step_number += 1 #将步数赋值 label_step_number[’text’] = ’步数:’ + str(step_number) #将步数变量导入label控件 '''交换按钮位置''' buttons[row_of_space,col_of_space][’text’] = buttons[x,y][’text’] buttons[x,y][’text’] = ’ ’ row_of_space = xcol_of_space = y n = 0 for row in range(3):for col in range(3): '''对比所有按钮序列是否正确,不正确则跳出函数''' if buttons[row,col][’text’] != numbers[n]: return n += 1 '''所有按钮判断完毕赢得游戏胜利''' label_welcomes[’text’] = ’你赢了’
这段是自定义了三个按钮的点击事件函数,不过三个都差不多,就是range后面的数字换了(应对不同的阶级)。这个函数在注释上已经写明了,是判断点击按钮旁是否有空白按钮的,有则交换位置。后面运用循环嵌套对比序列中的数字和矩阵上的是否一一对应,不对应就跳出循环,对应则判定为赢得游戏。
'''创建华容道游戏窗口'''root = Tk() #创建图形化用户界面实例root.title(’数字华容道’) #设置窗口标题root.geometry('400x400') #将窗口大小设为高300宽300root.configure(bg = ’black’) #将窗口背景设为黑色root.resizable(width = False,height = False) #设置窗口为不可拉伸'''设置欢迎语的label控件'''label_welcomes = Label(root,text = ’欢迎来到数字华容道’,bg = ’black’,fg = ’red’,font = ('Arial',13)) #设置label控件的属性label_welcomes.place(x = 20,y = 10,width = 250,height = 40) #设置label控件位置'''设置显示操作方式的label控件'''label_operation = Label(root,text = ’单击数字’,bg = ’black’,fg = ’white’,font = ('Arial',10))label_operation.place(x = 3,y = 40,width = 50,height = 30)label_operation_2 = Label(root,text = ’移动方块’,bg = ’black’,fg = ’white’,font = ('Arial',10))label_operation_2.place(x = 3,y = 60,width = 50,height = 30)'''设置显示步数的label控件'''label_step_number = Label(root,text = ’步数:’ + str(step_number),bg = ’black’,fg = ’yellow’,font = ('Arial',10))label_step_number.place(x = 3,y = 20,width = 50,height = 30)
这一段创建了图形化用户界面,具体每行代码做什么用的注释上我都标清楚了。
接着说一下,由于时间有限,只做了在壳窗口内选择几阶级数字华容道的版本。是用输入数字来判定的。其他的都是些简单玩意,比如说按钮创建,调用函数和循环嵌套,代码的注释上都写了一些大概意思,有点tkinter基础的应该都能看懂,不会的可以问我。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦网。
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备