Python 利用argparse模块实现脚本命令行参数解析
study.py内容如下
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = ’shouke’ import argparse def argparseFunc(): ’’’ 基于argparse模块实现命令参数解析功能 执行示例: python study.py -i 172.19.7.236 -p 8080 -a -r python study.py --ip 172.19.7.236 --port 7077 --auth -w -v True ’’’ parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='study.py usage help document') # 添加不带默认值的可解析参数 parser.add_argument('-i', '--ip', help='ip addr') #注意: -h、--help为内置参数,不可用 parser.add_argument('-p', '--port',help='host port') # 添加带默认值的可解析参数(# action = store_true 表示是如果使用了这个参数,则值参数值设置为True # 更多action配置可参考源码 # 需要注意的是,不能为带默认值参数指定参数值,会报错,该参数值会被当作不识别的参数 parser.add_argument('-a', '--auth', help='if auth need', action='store_true') # 添加互斥参数(比如 例中的-r和-w 同时只能用一个) exclusive_group = parser.add_mutually_exclusive_group() exclusive_group.add_argument('-r','--read', help='read enabled' , action='store_true') exclusive_group.add_argument('-w','--write', help='write enabled', action='store_true') # 添加参数时不设置设置参数说明 parser.add_argument(’-v’) # show verbose # 添加参数时不设置参数全名 parser.add_argument(’-V’, help='version') ARGS = parser.parse_args() # 获取命令行参数 print(’ARGS:’, ARGS) # 获取某个参数值 if ARGS.ip: # 注意,这里的参数名,必须使用参数全称 print('host addr is: %s' % ARGS.ip) if ARGS.port: print('host port is: : %s' % ARGS.port) if ARGS.auth: print('auth need: : %s' % ARGS.auth) if ARGS.read: print('read enabled: %s' % ARGS.read) if ARGS.write: print('write enabled: %s' % ARGS.write) argparseFunc()
运行测试
python study.py -i 172.19.7.236 -p 8080 -a -rpython study.py --ip 172.19.7.236 --port 7077 --auth -w -v True
结果如下
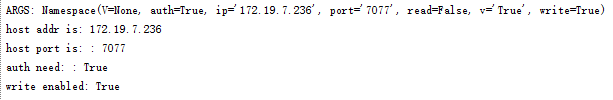
python study.py -i127.0.0.1 # 注意,参数和参数值之间可以没有空格
结果如下

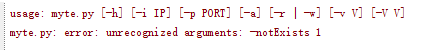
python study.py -notExists 1
结果如下
如上,以上代码实现是针对单个模块脚本,如果要在多个模块中使用咋办?解决方法为封装为类,具体参见“代码实践2”
#代码实践2
argument_parser.py #!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- ’’’@Author : shouke’’’ import argparse class ArgParser(object): ’’’ 参数解析器 ’’’ def __init__(self, none_exclusive_arguments, exclusive_arguments, description=’’): self.parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description=description) self.add_none_exclusive_arguments(none_exclusive_arguments) self.add_exclusive_arguments(exclusive_arguments) def add_none_exclusive_arguments(self, options:list): ’’’ 添加常规选项(非互斥选项) :param options 格式为list类型,形如 [ ’'-a', '--all', help='do not ignore entries starting with .'’, ’'-b', '--block', help='scale sizes by SIZE before printing them'’, ’'-C', '--color', help='colorize the output; WHEN can be ’never’, ’auto’'’, ’'-flag', help='make flag', action='store_true'’, # action='store_true' 表示如果不设置该选项的值,则默认值为true,类似的action='store_false' 表示默认值为false ] 其中,每个list元素为argparse.ArgumentParserlei add_argument类函数实参的字符串表示,add_argument函数定义add_argument(self, *args,**kwargs) ’’’ for option in options: eval(’self.parser.add_argument(%s)’ % option) def add_exclusive_arguments(self, options:list): ’’’ 添加互斥选项 :param options 格式为list,形如以下 [ (’'-r','--read',help='Read Action',action='store_true'’, ’'-w','--write',help='Write Action',action='store_true'’) ] ’’’ for option_tuple in options: exptypegroup = self.parser.add_mutually_exclusive_group() for item in option_tuple: eval(’exptypegroup.add_argument(%s)’ % item) @property def args(self): return self.parser.parse_args()
在xxx.py中引用(注意:为了让参数解析器起到应起的作用,建议在脚本最上方构造参数解析器对象)
study.py内容如下
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- __author__ = ’shouke’ from argument_parser import ArgParser none_exclusive_arguments = [ ’'-ip', help='自动化测试服务平台地址'’, ’'-projectId', help='自动化测试项目id'’, ’'-runEnv', help='自动化测试项目运行环境'’, ’'-logLevel', help='日志级别'’, ’'-masterHost', help='master服务地址'’, ’'-masterPort', help='master服务端口'’] exclusive_arguments = [ (’'-r', '--read', help='Read Action',action='store_true'’, ’'-w', '--write', help='Write Action',action='store_true'’)] args = ArgParser(none_exclusive_arguments, exclusive_arguments).args print(args)print(args.ip)print(args.read)
运行测试
python study.py -i 127.0.0.1 -r
运行结果如下

到此这篇关于Python 利用argparse模块实现脚本命令行参数解析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python 实现脚本命令行参数解析内容请搜索好吧啦网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦网!
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备