python实现与redis交互操作详解
本文实例讲述了python实现与redis交互操作。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
相关内容: redis模块的使用 安装模块 导入模块 连接方式 连接池 操作 设置值 获取值 管道 事务 订阅发布首发时间:2018-03-14 15:02
python可以使用redis模块来跟redis交互
redis模块的使用: 安装模块: pip3 install redis 导入模块:import redis 连接方式: 严格连接模式:r=redis.StrictRedis(host='',port=) 更Python化的连接模式:r=redis.Redis(host='',port=) StrictRedis用于实现大部分官方的命令,并使用官方的语法和命令 Redis与StrictRedis的区别是:Redis是StrictRedis的子类,用于向前兼容旧版本的redis-py,并且这个连接方式是更加'python化'的 连接池: 为了节省资源,减少多次连接损耗,连接池的作用相当于总揽多个客户端与服务端的连接,当新客户端需要连接时,只需要到连接池获取一个连接即可,实际上只是一个连接共享给多个客户端。import redispool= redis.ConnectionPool(host=’localhost’,port=6379,decode_responses=True)r=redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)r2=redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)r.set(’apple’,’a’)print(r.get(’apple’))r2.set(’banana’,’b’)print(r.get(’banana’))print(r.client_list())print(r2.client_list())#可以看出两个连接的id是一致的,说明是一个客户端连接 操作: 值的设置和获取,可以参考redis的命令,redis模块中的对应功能的函数名基本与redis中的一致 【注意默认情况下,设置的值或取得的值都为bytes类型,如果想改为str类型,需要在连接时添加上decode_responses=True】 设置值: redis中set() ==>r.set() redis中setnx() ==>r.set() redis中setex() ==>r.setex() redis中setbit() ==>r.setbit() redis中mset() == > r.mset() redis中hset() ==>r.hset() redis中sadd() == >r.sadd() 其他。。。基本redis的命令名与redis模块中的函数名一致 获取: redis中get() ==》r.get() redis中mget() ==》r.mget() redis中getset() ==》r.getset() redis中getrange() ==》r.getrange() 其他。。。基本redis的命令名与redis模块中的函数名一致
如果想要了解更多redis命令,可以参考我的另外一篇博文:
一文学redis操作(记录向)<点击即可跳转>import redisr=redis.Redis(host=’localhost’,port=6379,decode_responses=True)# r=redis.StrictRedis(host=’localhost’,port=6379)r.set(’key’,’value’)value=r.get(’key’)# print(type(value))print(value)r.hset(’info’,’name’,’lilei’)r.hset(’info’,’age’,’18’)print(r.hgetall(’info’))r.sadd(’course’,’math’,’english’,’chinese’)print(r.smembers(’course’))管道:
一般情况下,执行一条命令后必须等待结果才能输入下一次命令,管道用于在一次请求中执行多个命令。
参数介绍: transaction:指示是否所有的命令应该以原子方式执行。import redis,timer=redis.Redis(host='localhost',port=6379,decode_responses=True)pipe=r.pipeline(transaction=True)pipe.set(’p1’,’v2’)pipe.set(’p2’,’v3’)pipe.set(’p3’,’v4’)time.sleep(5)pipe.execute()事务:
python中可以使用管道来代替事务:
补充:监视watch:pipe.watch()import redis,timeimport redis.exceptionsr=redis.Redis(host=’localhost’,port=6379,decode_responses=True)pipe=r.pipeline()print(r.get(’a’))try: # pipe.watch(’a’) pipe.multi() pipe.set(’here’, ’there’) pipe.set(’here1’, ’there1’) pipe.set(’here2’, ’there2’) time.sleep(5) pipe.execute()except redis.exceptions.WatchError as e: print('Error')订阅发布: 发布方:
import redisr=redis.Redis(host='localhost',port=6379,decode_responses=True)#发布使用publish(self, channel, message):Publish ``message`` on ``channel``.Flag=Truewhile Flag: msg=input('主播请讲话>>:') if len(msg)==0: continue elif msg==’quit’: break else: r.publish(’cctv0’,msg) 订阅方: 当订阅成功后,第一次接收返回的第一个消息是一个订阅确认消息: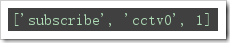
import redisr=redis.Redis(host='localhost',port=6379,decode_responses=True)#发布使用publish(self, channel, message):Publish ``message`` on ``channel``.Flag=Truechan=r.pubsub()#返回一个发布/订阅对象msg_reciver=chan.subscribe(’cctv0’)#订阅msg=chan.parse_response()#第一次会返回订阅确认信息print(msg)print('订阅成功,开始接收------')while Flag: msg=chan.parse_response()#接收消息 print('>>:',msg[2])#此处的信息格式[’消息类型’, ’频道’, ’消息’],所以使用[2]来获取
更多关于Python相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题:《Python常见数据库操作技巧汇总》、《Python编码操作技巧总结》、《Python数据结构与算法教程》、《Python Socket编程技巧总结》、《Python函数使用技巧总结》、《Python字符串操作技巧汇总》、《Python入门与进阶经典教程》及《Python文件与目录操作技巧汇总》
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。
相关文章:

 网公网安备
网公网安备