浅谈Java中File文件的创建以及读写
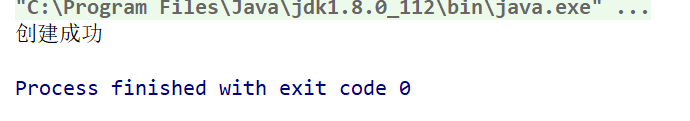
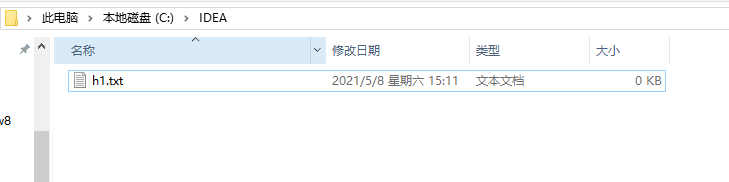
@Test public void test6() throws IOException {File file1 = new File('C:IDEAh1.txt');if(!file1.exists()){//文件不存在 file1.createNewFile(); System.out.println('创建成功');}else{//文件存在 file1.delete(); System.out.println('删除成功');} }
输出
file.mkdir,不会帮你创建上层目录 file.mkdirs,会帮你创建上层目录
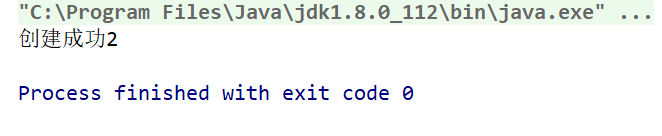
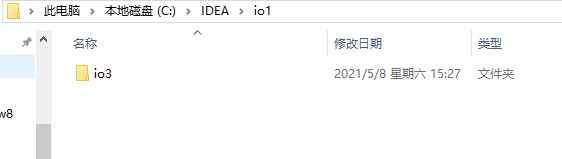
@Test public void test7(){//创建文件夹,mkdir,不会帮你创建上层目录File file1 = new File('c:IDEAio2');boolean mkdir =file1.mkdir();if(mkdir){ System.out.println('创建成功1');} //创建文件夹,mkdirs,会帮你创建上层目录File file2 = new File('c:IDEAio1io3');boolean mkdirs =file2.mkdirs();if(mkdirs){ System.out.println('创建成功2');} }
输出
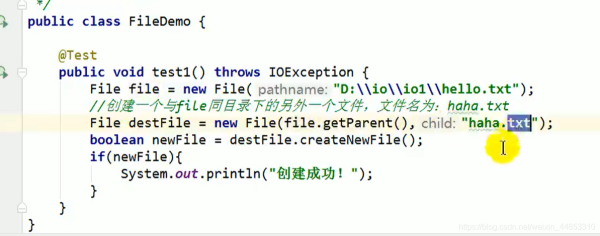
@Test public void test8(){//删除文件或空文件夹File file1 = new File('c:IDEAh1.txt'); file1.delete(); }5.递归删除所有文件(包括子文件)
//递归函数删除所有文件 private boolean deletedir(File dir){if (dir.isDirectory()) { File[] files = dir.listFiles(); //递归删除目录中的子目录下 for (File f:files) {boolean success = deletedir(f);if (!success) { return false;} }}// 目录此时为空,可以删除return dir.delete(); } @Test public void test8() {File dir = new File('c:IDEA');System.out.println(deletedir(dir)); }
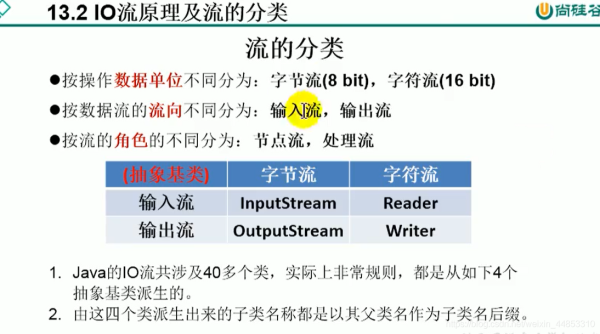
1.对于文本文件(.txt,.java,.c,.cpp),使用字符流处理
2.对于非文本文件(.jpg,.mp3,.mp4,.avi,.doc,.ppt)使用字节流处理
6.读取txt文件内容,流操作要用try-catch(字符流)@Testpublic void test9() { FileReader fr = null;//自动补的 try {//1.实例化File类的对象,指明要操作的文件File file1 = new File('c:IDEAhello.txt');file1.createNewFile();//要抛出异常//2.提供具体的流fr = new FileReader(file1);//3.数据的读入//read():返回读入的一个字符,如果达到文件末尾,返回-1int data = fr.read();while(data!=-1){ System.out.print((char)data); data = fr.read();} } catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace(); }finally {try { //4.流的关闭操作 if(fr!=null)//防止没有实例化成功,避免空指针异常fr.close();} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();} }
要记得关闭,因为物理连接JVM垃圾回收机制不会自动回收,要手动关闭。
7.读取文件内容升级方法(字符流)@Test public void test1() {FileReader fr = null;try { //1.File类的实例化 File file = new File('hello.txt'); //2.FileReader流的实例化 fr = new FileReader(file); //3.读入的操作 //read(char[] cbuf):返回每次读入cbuf数组中的字符的个数。如果达到文件末尾,返回-1 char[] cbuf = new char[5]; int len; while ((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {//错误的写法//for(int i=0;i<cbuf.length;i++{// System.out.println(cbuf[i]);//} //正确的写法for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) { System.out.println(cbuf[i]);} }} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();} finally { if (fr != null)try { //4.资源的关闭 fr.close();} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();}} }
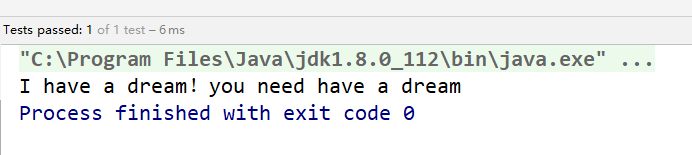
@Test public void test2() throws IOException{//File对应的硬盘中的文件// 如果不存在,在输出的过程中,会自动创建此文件//1.提供File类的对象,指明写出到的文件FileWriter fw = null;try { File file = new File('hello.txt'); //2.提供FileWriter的对象,用于数据的写出 //FileWriter(file,append)第二个参数,append是true则在后面添加,是false就覆盖 fw = new FileWriter(file,true); //3.写出的操作 fw.write('I have a dream!'); fw.write('you need have a dream');} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();} finally { try {if(fw!=null)//4.流资源的关闭fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace(); }}}
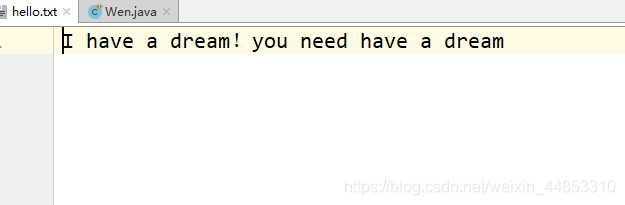
@Test public void test3(){FileReader fr = null;FileWriter fw = null;try { // 1.创建File类的对象,指明读入和写出的文件 File src = new File('hello.txt'); File des = new File('hello1.txt'); // 2.创建输入输出流的对象 fr = new FileReader(src); fw = new FileWriter(des,true);//不覆盖 // 3.数据的读入和写出操作 char[] cbuf = new char[5]; int len; while((len = fr.read(cbuf))!=-1){//每次写出len个字符fw.write(cbuf,0,len);//从cbuf的0号位开始写入len个字符 }} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();} finally { try {// 4.关闭流资源1fw.close(); } catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace(); } try {// 4.关闭流资源2fr.close(); } catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace(); }} }
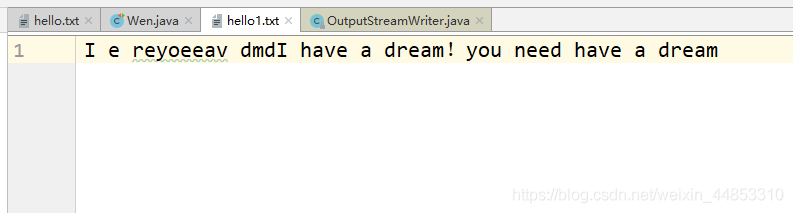
@Test public void test4(){FileInputStream fis=null;FileOutputStream fos=null;try { //1.造文件 File src = new File('b.jpg'); File des = new File('c.jpg'); //2.造流 fis = new FileInputStream(src); fos = new FileOutputStream(des); //3.读数据,存数据 byte[] buffer = new byte[5]; int len;//记录每次读取的字节的个数 while((len = fis.read(buffer))!=-1){fos.write(buffer,0,len); }} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();} finally { if(fos!=null) {try { //4.关闭资源 fos.close();} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();} } if(fis!=null) {try { //4.关闭资源 fis.close();} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();} }} }
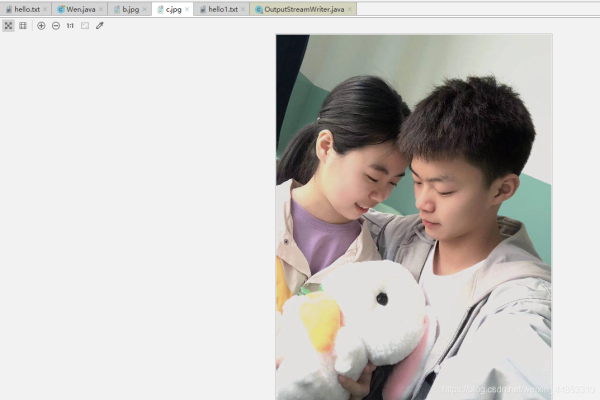
@Test public void test5(){BufferedInputStream bis = null;BufferedOutputStream bos = null;try { //1.造文件 File src = new File('b.jpg'); File des = new File('d.jpg'); //2.造流 //2.1造节点流 FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(src); FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(des); //2.2造缓冲流 bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis); bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos); //3.复制的细节:读取,写入 byte[] buffer =new byte[10]; int len; while((len=bis.read(buffer))!=-1){bos.write(buffer,0,len); }} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();} finally { //4.资源关闭 //要求,先关闭外层的流,再关闭内层的流 if(bos!=null){try { bos.close();} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();} } if(bis!=null){try { bis.close();} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();} } //说明:关闭外层流的同时,内层自动关闭,所以外层关闭可以省略 //fos.close(); //fis.close();} }
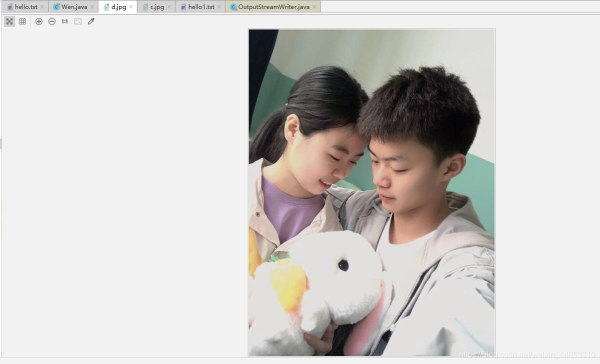
用缓冲流快了很多

经典步骤:
1.创建File类的对象,指明读入和写出的文件
2.创建输入输出流的对象
3.数据的读入和写出操作
4.关闭流资源
到此这篇关于浅谈Java中File文件的创建以及读写的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java中File文件的创建及读写内容请搜索好吧啦网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦网!
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备