Java容器源码LinkedList原理解析
LinkedList简介
LinkedList是一个使用双向链表结构实现的容器,与ArrayList一样,它能动态扩充其长度,LinkedList相较于ArrayList,其任意位置插入速度比ArrayList要快,但是其查询速度要比ArrayList要慢;LinkedList继承自AbstractSequentialList,实现了List、Deque、Cloneable、Serializable接口。
LinkedList UML图如下:
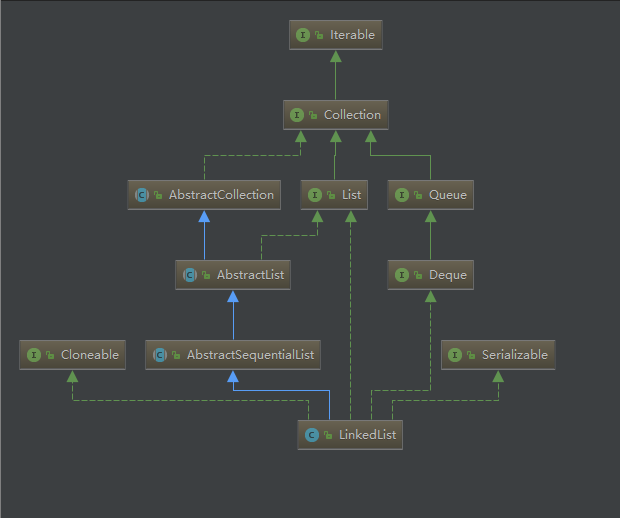
和ArrayList一样,LinkedList也不是一个线程安全的容器。
LinkedList源码分析
构造方法
LinkedList有两个构造方法:
public LinkedList() {}//从已有的一个容器创建一个LinkedList对象public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c);}
addAll()方法:
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { return addAll(size, c);}public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { //检查index是否溢出 checkPositionIndex(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0) return false; //获取第index位置的node元素和node的前一个元素 //succ:第index位置的node元素 //pred:index位置前一个node元素 Node<E> pred, succ; if (index == size) { succ = null; pred = last; } else { succ = node(index); pred = succ.prev; } //遍历,将元素插入链表中 for (Object o : a) { @SuppressWarnings('unchecked') E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; pred = newNode; } if (succ == null) { last = pred; } else { pred.next = succ; succ.prev = pred; } size += numNew; modCount++; return true;}
add方法
LinkedList也有两个add方法,如下:
public boolean add(E e) { //添加元素到队尾 linkLast(e); return true;}public void add(int index, E element) { //检查index是否溢出 checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) //index == size,直接添加到队尾 linkLast(element); else //index != size,添加元素到index位置 linkBefore(element, node(index));}
linkLast方法:
void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; //新建一个node,将其前一个元素指针指向原链表的最后一个元素 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); //更新尾指针 last = newNode; if (l == null) //若原last==null说明此时链表就一个元素 first = newNode; else //更新原链表尾元素指针 l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++;}
linkBefore方法:
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { // assert succ != null; //获取指定位node元素的前一个元素pred final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; //新建一个node,将其前指针指向pred元素 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); //将指定位置的node元素的前指针指向新元素,完成插入 succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++;}
获取指定位置node指针方法node:
Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); //index > size/2时,说明在链表前半段,从前往后搜索 if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; //index < size/2时,从后往前搜索 } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; }}
get方法也比较简单,首先检测index是否溢出,然后直接找到index位置的元素,并返回其item。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦网。
相关文章:
1. 在 XSL/XSLT 中实现随机排序2. CSS Hack大全-教你如何区分出IE6-IE10、FireFox、Chrome、Opera3. XML在语音合成中的应用4. chatGPT教我写compose函数的详细过程5. 用css截取字符的几种方法详解(css排版隐藏溢出文本)6. asp(vbs)Rs.Open和Conn.Execute的详解和区别及&H0001的说明7. JavaScript避免嵌套代码浅析8. Vue Element UI 表单自定义校验规则及使用9. 《CSS3实战》笔记--渐变设计(一)10. CSS3实例分享之多重背景的实现(Multiple backgrounds)
 网公网安备
网公网安备