Android如何获取子View的位置及坐标详解
一、View
1.1、View 概述
视图 (View) 是一个容器,专门负责布局。表现为显示在屏幕上的各种视图,如 TextView、LinearLayout 等。
1.2、View 分类
View 主要分为两类,具体如下表格所示:
类别 示例 特点 单一视图 即一个 View,如 TextView、EditText 不包含子View 视图组 即多个 View 组成的 ViewGroup,如 RelativeLayout 包含子View
1.3、View 类简介
View 类是 Android 中各种组件的基类;
View 的构造函数有四个,具体如下所示:
public View(Context context) {}public View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0);}public View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { this(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, 0);} public View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) { }
源码中 View 的构造函数
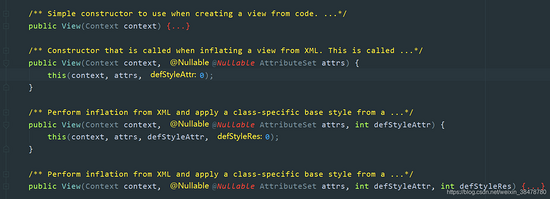
通过源码的注释我们可以看出:
如果 View 是在 Java 代码里面 new 的,则调用第一个构造函数-->View(Context); 如果 View 是在 xml 里声明的,则调用第二个构造函数-->View(Context, AttributeSet)。二、Android 坐标系
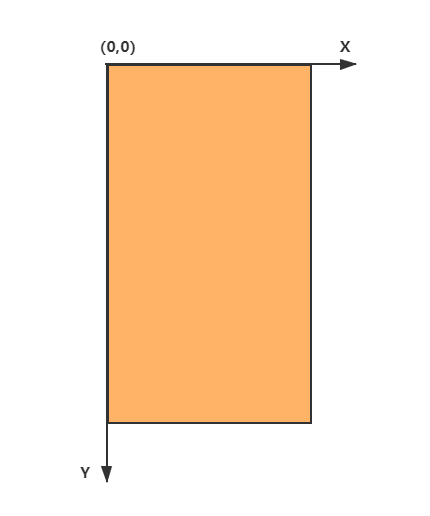
Android 坐标系和数学上的坐标系是不一样的,定义如下:
屏幕的左上角为坐标原点。 向右为 x 轴增大方向。 向下为 y 轴增大方向。具体如下图所示:
三、View 的位置
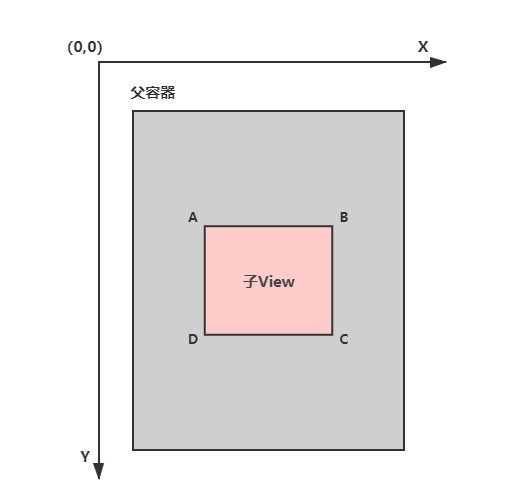
View 的位置是相对于父控件而言的,由 4 个顶点确定,如下图 A、B、C、D 所示:
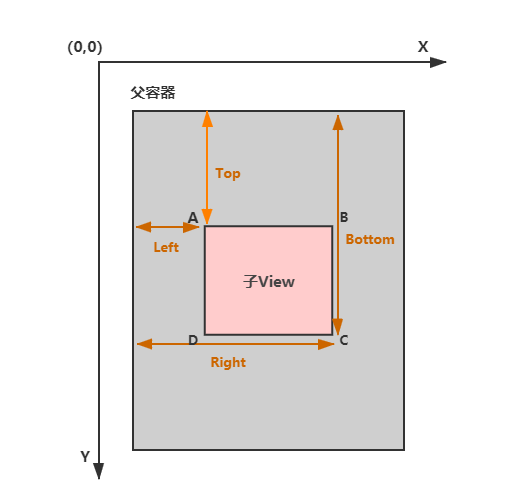
确定 View 的位置有四个参数,分别是 Top、Bottom、Left、Right:
Top:子 View 左上角距父 View 顶部的距离。 Left:子 View 左上角距父 View 左侧的距离。 Bottom:子 View 右下角距父 View 顶部的距离。 Right:子 View 右下角距父 View 左侧的距离具体如下图所示:
四、获取 View 位置的方式
View 的位置是通过 getTop()、getLeft()、getBottom()、getRight() 函数进行获取的。
这里我写了一个小例子来演示这四个方法,如下所示:(获取内部子 View 的位置)

因为是为了演示 View 的位置,所有我这里用绝对布局,并且大小的单位都是用 px,具体布局如下所示:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?><AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android='http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android' xmlns:app='http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto' xmlns:tools='http://schemas.android.com/tools' android:layout_width='match_parent' android:layout_height='match_parent' tools:context='.MainActivity'> <RelativeLayout android: android:layout_width='600px' android:layout_height='600px' android:layout_x='200px' android:layout_y='200px' android:background='@color/colorPrimaryDark'> <View android: android:layout_width='300px' android:layout_height='300px' android:layout_centerInParent='true' android:background='@color/colorAccent' /> </RelativeLayout></AbsoluteLayout>
我们现在用四个方法来获取一下 View 的位置,具体代码如下所示:
public class CoordinateActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private View mView; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_coordinate); rl1 = findViewById(R.id.rl_1); mView = findViewById(R.id.view); } @Override protected void onResume() { super.onResume(); new Handler().postDelayed(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { MyLogUtils.i(mView.getTop() + '--Top --mView'); MyLogUtils.i(mView.getBottom() + '--Bottom --mView'); MyLogUtils.i(mView.getLeft() + '--Left --mView'); MyLogUtils.i(mView.getRight() + '--Right --mView'); MyLogUtils.i(mView.getX() + '--X --mView'); MyLogUtils.i(mView.getY() + '--Y --mView'); } }, 200); }}
打印结果如下所示:
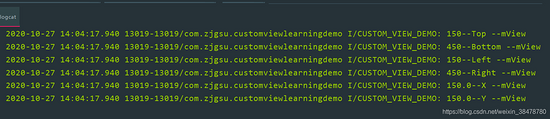
最外层紫色的 View 的坐标是(200,200),大小是 600px,在它内部,有一个大小为 300px 的子 View 位于其中心位置,所以上述打印结果是完全正确的。
注意:
我这里调用 getTop() 等方法是在 onResume() 里面,并且延时了 200ms,是因为如果不延迟直接调用,会出现 View 还没有绘制完,所以获取到的位置都是 0,所以就用最简单的延迟处理了一下(这里的处理方法有很多,比如 View.post() 等); getX() 和 getY() 的意思是获取子 View 相对父容器的坐标,所以这里结果都是 150。总结
到此这篇关于Android如何获取子View的位置及坐标的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android获取子View位置及坐标内容请搜索好吧啦网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦网!
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备