基于SpringBoot服务端表单数据校验的实现方式
SpringBoot服务端表单数据校验
(SpringBoot高级)
一、实现添加用户功能1 创建项目
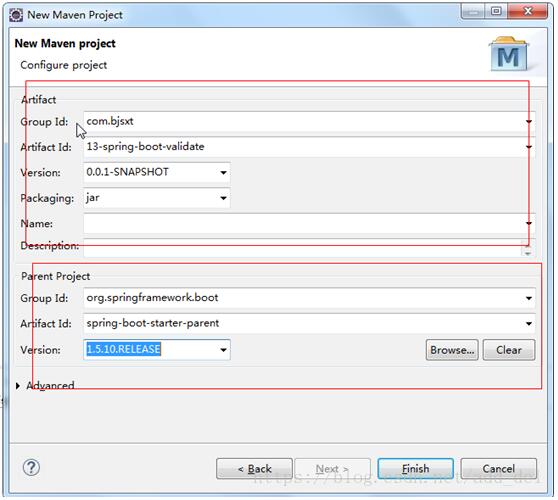
2 修改POM文件
<project xmlns='http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0' xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance' xsi:schemaLocation='http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd'> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>1.5.10.RELEASE</version> </parent> <groupId>com.bjsxt</groupId> <artifactId>13-spring-boot-validate</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <properties> <java.version>1.7</java.version> <thymeleaf.version>3.0.2.RELEASE</thymeleaf.version> <thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>2.0.4</thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!-- springBoot的启动器 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!-- thymeleaf的启动器 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies></project>
3 编写添加用户功能
3.1 创建实体类
publicclass Users { private String name; private String password; private Integer age; public String getName() { returnname; } publicvoid setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { returnpassword; } publicvoid setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public Integer getAge() { returnage; } publicvoid setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return'Users [name=' + name + ', password=' + password + ', age=' + age + ']'; } }
3.2 编写Controller
/** * SpringBoot 表单数据校验 * * */@Controllerpublicclass UsersController { @RequestMapping('/addUser') public String showPage(){ return'add'; } /** * 完成用户添加 */ @RequestMapping('/save') public String saveUser(Users users){ System.out.println(users); return'ok'; }}
3.3 编写页面add.html ok.html
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset='UTF-8'><title>添加用户</title></head><body> <form th:action='@{/save}' method='post'> 用户姓名:<input type='text' name='name'/><br/> 用户密码:<input type='password' name='password' /><br/> 用户年龄:<input type='text' name='age' /><br/> <input type='submit' value='OK'/> </form></body></html><!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset='UTF-8'><title>操作成功</title></head><body> OK。。。。</body></html>二、SpringBoot对表单做数据校验
1 SpringBoot对表单数据校验的技术特点
1.1 SpringBoot中使用了Hibernate-validate校验框架
2 SpringBoot表单数据校验步骤
2.1 在实体类中添加校验规则
publicclass Users { @NotBlank//非空校验 private String name; @NotBlank//密码非空校验 private String password; private Integer age; public String getName() { returnname; } publicvoid setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { returnpassword; } publicvoid setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public Integer getAge() { returnage; } publicvoid setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return'Users [name=' + name + ', password=' + password + ', age=' + age + ']'; } }
2.2 在Controller中开启校验
/** * 完成用户添加 *@Valid开启对Users对象的数据校验 *BindingResult:封装了校验的结果 */ @RequestMapping('/save') public String saveUser(@Valid Users users,BindingResult result){ if(result.hasErrors()){ return'add'; } System.out.println(users); return'ok'; }
2.3 在页面中获取提示信息
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset='UTF-8'><title>添加用户</title></head><body> <form th:action='@{/save}' method='post'> 用户姓名:<input type='text' name='name'/><font color='red' th:errors='${users.name}'></font><br/> 用户密码:<input type='password' name='password' /><font color='red' th:errors='${users.password}'></font><br/> 用户年龄:<input type='text' name='age' /><font color='red' th:errors='${users.age}'></font><br/> <input type='submit' value='OK'/> </form></body></html>
2.4 遇到异常
在jsp当中,如果一个对象根本不存在,那么他仍然可以在jsp页面进行遍历,只不过为空,不显示而已,但是在thymeleaf当中,如果说这个对象不存在,他就会报以下错误,解决问题的办法就是在controller中的方法上的传递参数加上这个对象,以便在thymeleaf视图层当中,告知这个对象是存在于的

解决异常的方法,在跳转页面的方法中注入一个对象,来解决问题。要求参数对象的变量名必须是对象的类名的全称首字母小写。
在springboot 1.5当中,参数变量必须是对象类的名称首字母小写,但是在springboot2.0以上,已经很大程度上优化了这个问题,变量名称随便写,因为在跳转页面的时候,将该对象放入到Model当中传递,他的key 就是对象的类的全程首字母大写(默认),在thymeleaf当中取出这个值的时候,他的key为对象的类的全程首字母大写,与参数的变量名无任何关系 如果非要更改Model当中的key值,一下有详解
代码
/** * 解决异常的方式。可以在跳转页面的方法中注入一个Uesrs对象。 * 注意:由于springmvc会将该对象放入到Model中传递。key的名称会使用该对象的驼峰式的命名规则来作为key。 * 参数的变量名需要与对象的名称相同。将首字母小写。 * * @param users * @return */ @RequestMapping('/addUser') public String showPage( Users users){ return'add'; }/** * 完成用户添加 *@Valid开启对Users对象的数据校验 *BindingResult:封装了校验的结果 */ @RequestMapping('/save') public String saveUser( @Valid Users users,BindingResult result){ if(result.hasErrors()){ return'add'; } System.out.println(users); return'ok'; }
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset='UTF-8'><title>添加用户</title></head><body> <form th:action='@{/save}' method='post'> 用户姓名:<input type='text' name='name'/><font color='red' th:errors='${users.name}'></font><br/> 用户密码:<input type='password' name='password' /><font color='red' th:errors='${users.password}'></font><br/> 用户年龄:<input type='text' name='age' /><font color='red' th:errors='${users.age}'></font><br/> <input type='submit' value='OK'/> </form></body></html>
如果参数的名称需要做改变
/** * * 如果想为传递的对象更改名称,可以使用@ModelAttribute('aa')这表示当前传递的对象的key为aa。 * 那么我们在页面中获取该对象的key也需要修改为aa * @param users * @return */ @RequestMapping('/addUser') public String showPage(@ModelAttribute('aa') Users users){ return'add'; }/** * 完成用户添加 *@Valid开启对Users对象的数据校验 *BindingResult:封装了校验的结果 */ @RequestMapping('/save') public String saveUser(@ModelAttribute('aa') @Valid Users users,BindingResult result){ if(result.hasErrors()){ return'add'; } System.out.println(users); return'ok'; }
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><meta charset='UTF-8'><title>添加用户</title></head><body> <form th:action='@{/save}' method='post'> 用户姓名:<input type='text' name='name'/><font color='red' th:errors='${aa.name}'></font><br/> 用户密码:<input type='password' name='password' /><font color='red' th:errors='${aa.password}'></font><br/> 用户年龄:<input type='text' name='age' /><font color='red' th:errors='${aa.age}'></font><br/> <input type='submit' value='OK'/> </form></body></html>四、其他校验规则
@NotBlank: 判断字符串是否为null或者是空串(去掉首尾空格)。
@NotEmpty: 判断字符串是否null或者是空串。
@Length: 判断字符的长度(最大或者最小)
@Min: 判断数值最小值
@Max: 判断数值最大值
@Email: 判断邮箱是否合法
补充知识:控制Configuration是否生效,使用Springboot中@ConditionalOnProperty注解
介绍
@ConditionalOnProperty注解的作用是来控制Configuration是否生效
通过其两个属性name以及havingValue来实现的,其中name用来从application.properties中读取某个属性值。
matchIfMissing来控制默认值
如果值不为空,则将该值与havingValue指定的值进行比较,如果一样则返回true;否则返回false。
如果返回值为false,则该configuration不生效;为true则生效。
使用
shardingjdbc中可以控制是否启用,这样可以针对某个配置来启动数据源,完全不影响代码实现,想完成这个功能就要用到Stringboot提供的注解@ConditionalOnProperty
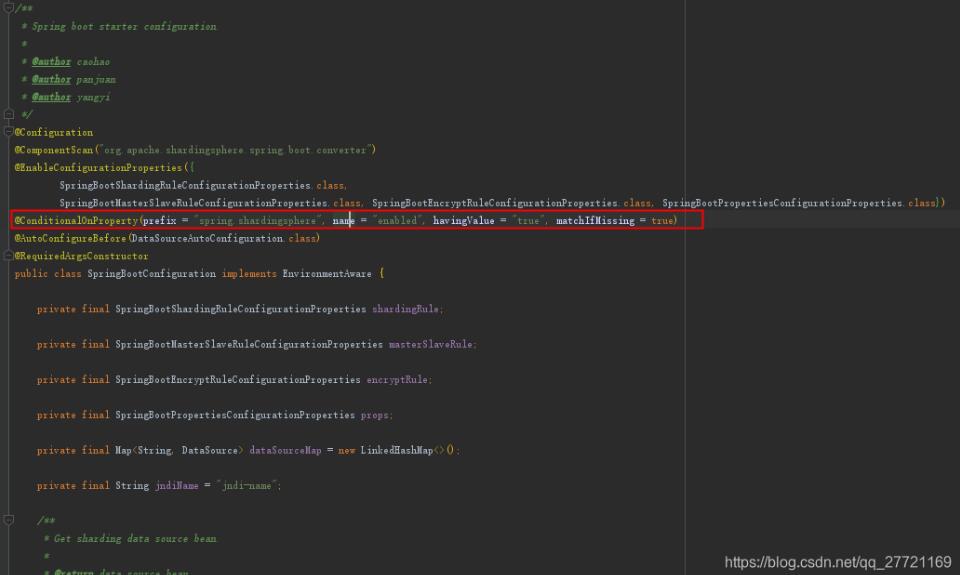
因为默认是true,所以使用可以忽略,但是如果不需要使用,禁用则需要增加配置
spring.shardingsphere.enabled=false
以上这篇基于SpringBoot服务端表单数据校验的实现方式就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦网。
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备