SpringBoot @Validated注解实现参数分组校验的方法实例
前言
在前后端分离开发的时候我们需要用到参数校验,前端需要进行参数校验,后端接口同样的也需要,以防传入不合法的数据。
1、首先还是先导包,导入pom文件。
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId></dependency>
2、解释一下注解的作用
@Null 限制只能为null@NotNull 限制必须不为null@NotEmpty 只作用于字符串类型,字符串不为空,并且长度不为0@NotBlank 只作用于字符串类型,字符串不为空,并且trim()后不为空串@AssertFalse 限制必须为false@AssertTrue 限制必须为true@DecimalMax(value) 限制必须为一个不大于指定值的数字@DecimalMin(value) 限制必须为一个不小于指定值的数字@Digits(integer,fraction) 限制必须为一个小数,且整数部分的位数不能超过integer,小数部分的位数不能超过fraction@Future 限制必须是一个将来的日期@Past 验证注解的元素值(日期类型)比当前时间早@Max(value) 限制必须为一个不大于指定值的数字@Min(value) 限制必须为一个不小于指定值的数字@Pattern(value) 限制必须符合指定的正则表达式@Size(max,min) 限制字符长度必须在min到max之间@Email 验证注解的元素值是Email,也可以通过正则表达式和flag指定自定义的email格式
3、在实体类加上要验证的字段。(我这里随便写下)
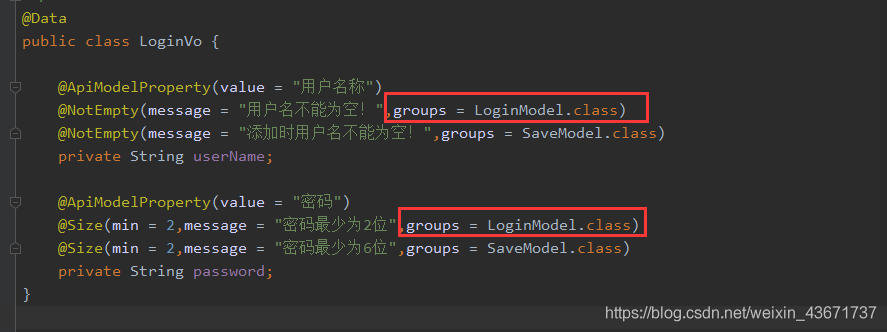
标注的地方就是用来分组校验的,下下面会解释。
@Datapublic class LoginVo { @ApiModelProperty(value = '用户名称') @NotEmpty(message = '用户名不能为空!',groups = LoginModel.class) @NotEmpty(message = '添加时用户名不能为空!',groups = SaveModel.class) private String userName; @ApiModelProperty(value = '密码') @Size(min = 2,message = '密码最少为2位',groups = LoginModel.class) @Size(min = 6,message = '密码最少为6位',groups = SaveModel.class) private String password;}
通过groups的属性来分组,假设我在使用登录分组校验的时候,设定用户名不能为空和密码最少为2位的验证。而在添加分组设定添加时用户名不能为空和密码最少为6位的验证。
4、在来解释下上面标注的分组接口。
LoginModel
import javax.validation.groups.Default;public interface LoginModel extends Default {}
必须继承默认的Defaut接口不然后抛出异常。
SaveModel
import javax.validation.groups.Default;public interface SaveModel extends Default{}
5、在controller的接口上加上@Validated注解,参数就加上你需要根据那种规则来校验。
@ApiOperation(value = '登录以后返回token') @PostMapping(value = '/login') public Result login(@RequestBody @Validated(LoginModel.class) LoginVo loginVo) { String token = userService.login(loginVo.getUserName(), loginVo.getPassword()); return Result.success(token); }
运行后只能在控制台显示错误的结果,新的问题又来了怎么把错误的结果通过自己的result类返回给前端。这就需要对错误全局捕捉了。
6、写一个对Response换回结果的处理。
@RestControllerAdvice@Slf4jpublic class ParameterCalibration { @ExceptionHandler({MethodArgumentNotValidException.class, BindException.class}) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) @ResponseBody public Result handleMethodArgumentNotValidException(Exception exception) { StringBuilder errorInfo = new StringBuilder(); BindingResult bindingResult=null; if(exception instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException){ bindingResult= ((MethodArgumentNotValidException)exception).getBindingResult(); } if(exception instanceof BindException){ bindingResult= ((BindException)exception).getBindingResult(); } for(int i = 0; i < bindingResult.getFieldErrors().size(); i++){ if(i > 0){errorInfo.append(','); } FieldError fieldError = bindingResult.getFieldErrors().get(i); errorInfo.append(fieldError.getField()).append(' :').append(fieldError.getDefaultMessage()); } log.error(errorInfo.toString()); //这里返回自己的Result的结果类。 return Result.validateFailed(errorInfo.toString()); } @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST) @ResponseBody public Result handleDefaultException(Exception exception) { log.error(exception.toString()); //这里返回自己的Result的结果类。 return Result.validateFailed('服务器错误',exception); }}
``
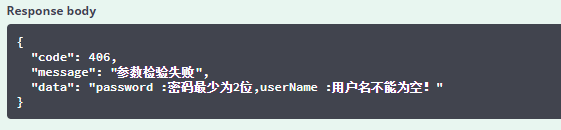
7. 先测试LoginModel的校验规则
控制台打印的数据

前端收到的数据
切换成SaveModel控制台打印的数据

切换成SaveModel前端收到的数据
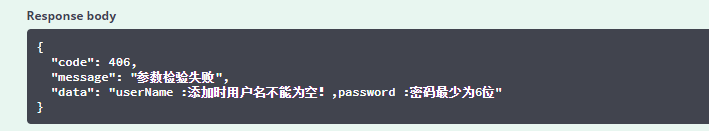
可以看到两次的验证规则时不同的,完成了简易的分组操作。
8 、总结,就是在添加验证规则的时候指定对应的分组,在使用时传入需要的分组。可能理解有误,发现请指导。
总结
到此这篇关于SpringBoot @Validated注解实现参数分组校验的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringBoot @Validated注解实现参数分组校验内容请搜索好吧啦网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦网!
相关文章:

 网公网安备
网公网安备