Springboot hibernate envers使用过程详解
添加maven配置
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?><project xmlns='http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0' xmlns:xsi='http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance' xsi:schemaLocation='http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd'> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version> </parent> <artifactId>springboot-envers</artifactId> <name>springboot-envers</name> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> <artifactId>hibernate-envers</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.h2database</groupId> <artifactId>h2</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies></project>
使用User类作为被审计的对象
@Entity@Table(name = 'user')@Audited@JsonIgnoreProperties(value = 'hibernateLazyInitializer')public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue private Long id; private String name; public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }}
添加配置
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=createspring.jpa.properties.org.hibernate.envers.audit_strategy=org.hibernate.envers.strategy.internal.ValidityAuditStrategyspring.jpa.properties.org.hibernate.envers.audit_strategy_validity_store_revend_timestamp=truespring.h2.console.enabled=truespring.h2.console.path=/h2spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:enversspring.datasource.username=saspring.datasource.password=saspring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
创建相应的UserRepository
@Repositorypublic interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {}
添加用于增删改的Controller
@Controllerpublic class UserController { @Autowired private UserRepository userRepository; private int counter; @ResponseBody @RequestMapping('/user/add') public Object add() { User user = new User(); user.setName('name' + ++counter); userRepository.save(user); return user; } @ResponseBody @RequestMapping('/user/update/{id}') public Object update(@PathVariable Long id) { User user = userRepository.getOne(id); user.setName('name' + ++counter); userRepository.save(user); return user; } @ResponseBody @RequestMapping('/user/delete/{id}') public Object delete(@PathVariable Long id) { User user = userRepository.getOne(id); userRepository.delete(user); return user; }}
添加启动类
@SpringBootApplicationpublic class SpringbootEnversApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(SpringbootEnversApplication.class, args); }}
运行程序后,访问http://localhost:8080/h2,输入密码sa,即可登陆数据库并查询数据
由于配置了spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=create,可以看到系统已经为我们生成了相关的数据表
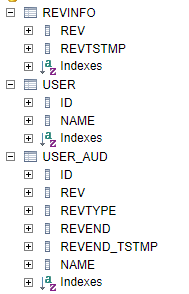
其中USER是实体类的表,USER_AUD是对应的审计表
依次访问以下链接,增加两条数据,分别对两条数据进行更新,再删除第一条数据
http://localhost:8080/user/add
http://localhost:8080/user/add
http://localhost:8080/user/update/1
http://localhost:8080/user/update/2
http://localhost:8080/user/delete/1
在h2页面查询USER表
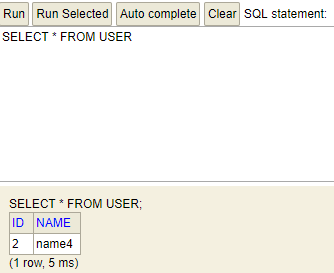
可以看到,USER表只有第二条数据更新后的记录了
而查询USER_AUD表
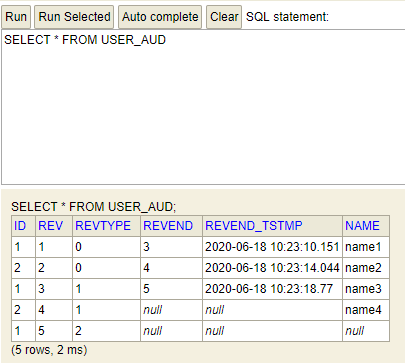
可以看到表中存在5条记录,分别对应着上面的五次操作
其中ID是USER表的主键,REV是USER_AUD的主键,REVTYPE是操作类型,0新增,1更新,2删除,name则是对应USER的name属性
hibernate提供了两种审计策略,分别是
org.hibernate.envers.strategy.internal.DefaultAuditStrategy org.hibernate.envers.strategy.internal.ValidityAuditStrategy如果使用DefaultAuditStrategy,USER_AUD表中不会有REVEND,REVEND_TSTMP两个字段,只会单纯的记录变更与版本
而使用ValidityAuditStrategy,在新增一条变更记录时,会更新上一条变更记录的REVEND,REVEND_TSTMP为当前的版本号以及变更时间
因为ValidityAuditStrategy除了插入新纪录还要更新旧的记录,所以插入速度会慢一点,但是因为提供了额外的信息,对于数据查询,速度则较DefaultAuditStrategy更快一些
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦网。
相关文章:

 网公网安备
网公网安备