Spring Boot两种全局配置和两种注解的操作方法
1、掌握application.properties配置文件
2、掌握application.yaml配置文件
3、掌握使用@ConfigurationProperties注入属性
4、掌握使用@Value注入属性
一、全局配置文件概述全局配置文件能够对一些默认配置值进行修改。Spring Boot使用一个application.properties或者application.yaml的文件作为全局配置文件,该文件存放在src/main/resource目录或者类路径的/config,一般会选择resource目录。
二、Application.properties配置文件(一)创建Spring Boot的Web项目PropertiesDemo
利用Spring Initializr方式创建项目
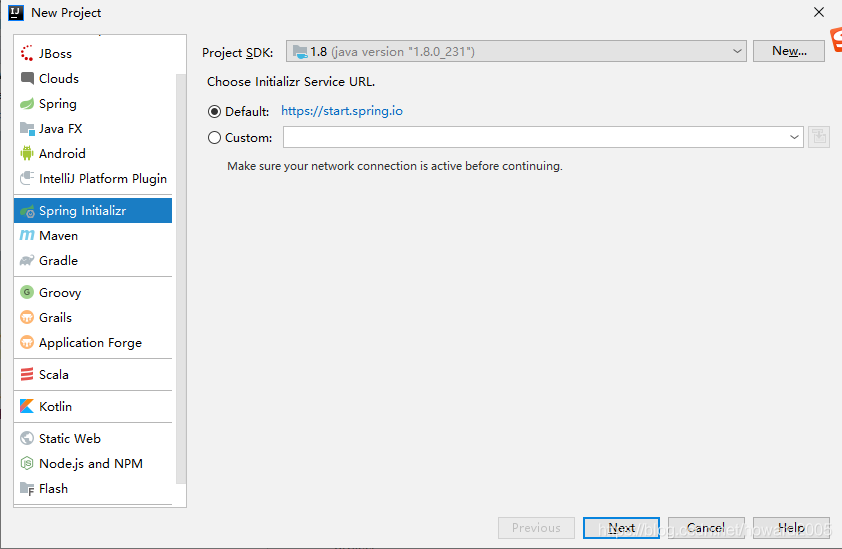
设置项目元数据
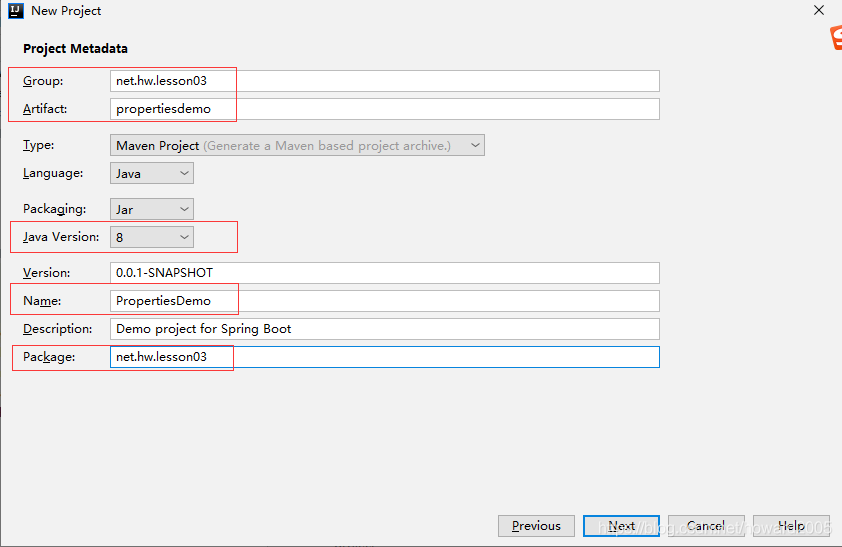
添加测试和Web依赖
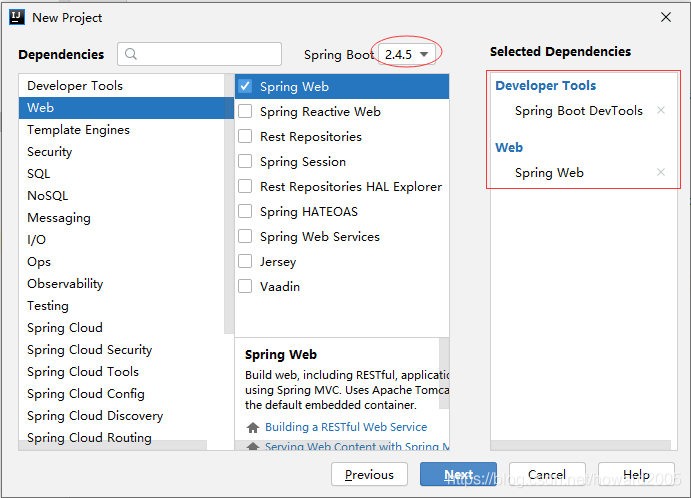
设置项目名称及保存位置
单击【Finish】按钮,完成项目初始化工作
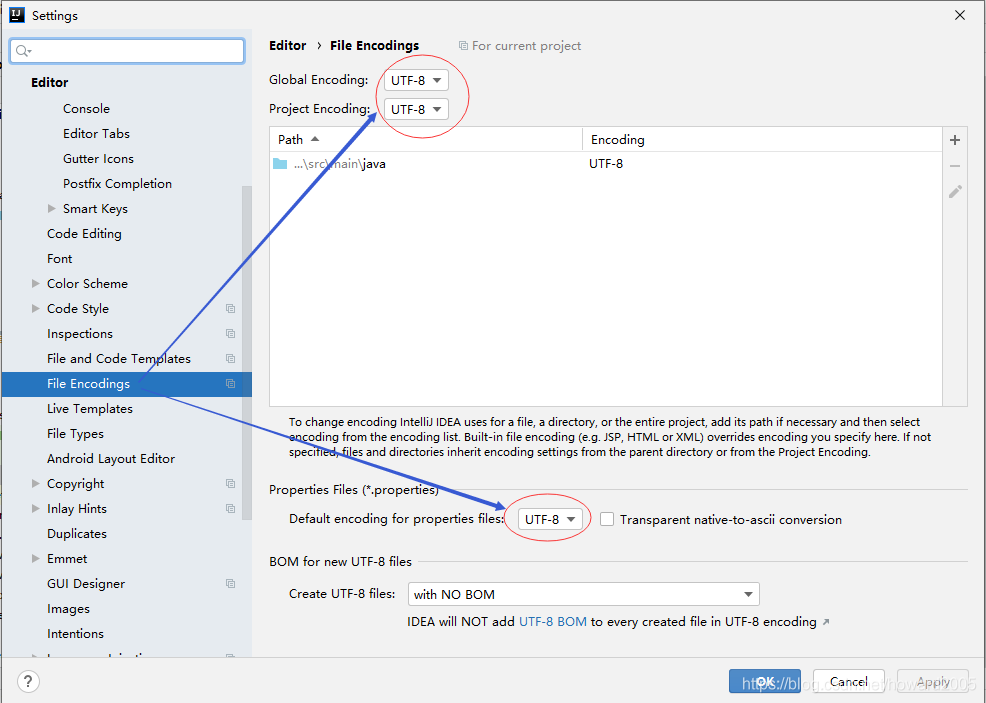
设置项目编码为utf8
(二)在application.properties里添加相关配置 点开resource目录,查看应用程序属性配置文件
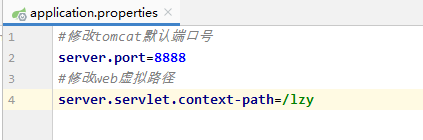
#修改tomcat默认端口号server.port=8888#修改web虚拟路径server.servlet.context-path=/lzy
更多配置属性,详见官网https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/common-application-properties.html启动应用,查看控制台
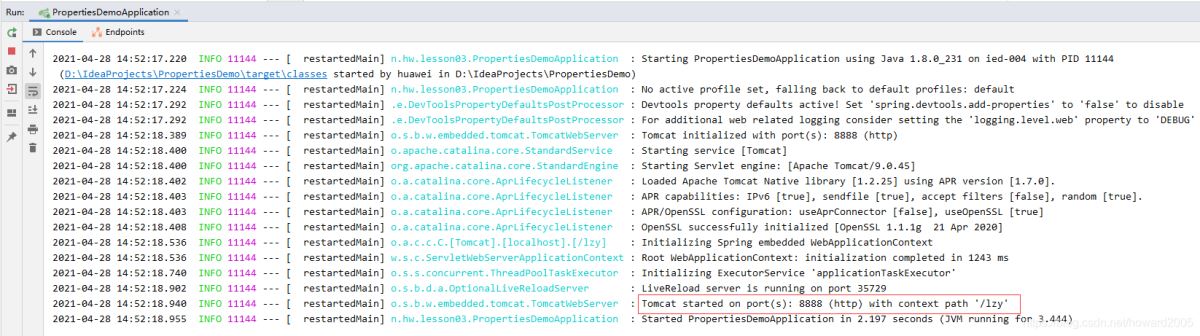
(1)创建Pet类
在net.hw.lesson03里创建bean子包,在子包里创建Pet类
package net.hw.lesson03.bean; /** * 功能:宠物实体类 * 作者:华卫 * 日期:2021年04月28日 */public class Pet { private String type; // 类型 private String name; // 名字 public String getType() {return type; } public void setType(String type) {this.type = type; } public String getName() {return name; } public void setName(String name) {this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() {return 'Pet{' +'type=’' + type + ’’’ +', name=’' + name + ’’’ +’}’; }}
(2)创建Person类
在net.hw.lesson03.bean包里创建Person类
package net.hw.lesson03.bean; import java.util.List;import java.util.Map; /** * 功能:人类 * 作者:华卫 * 日期:2021年04月28日 */public class Person { private int id; // 编号 private String name; // 姓名 private List<String> hobby; // 爱好; private Map<String, String> family; // 家庭成员 private Pet pet; // 宠物 public int getId() {return id; } public void setId(int id) {this.id = id; } public String getName() {return name; } public void setName(String name) {this.name = name; } public List<String> getHobby() {return hobby; } public void setHobby(List<String> hobby) {this.hobby = hobby; } public Map<String, String> getFamily() {return family; } public void setFamily(Map<String, String> family) {this.family = family; } public Pet getPet() {return pet; } public void setPet(Pet pet) {this.pet = pet; } @Override public String toString() {return 'Person{' +'id=' + id +', name=’' + name + ’’’ +', hobby=' + hobby +', family=' + family +', pet=' + pet +’}’; }}
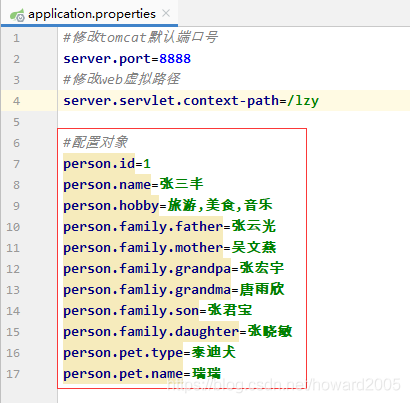
(3)在application.properties里配置对象
#配置对象person.id=1person.name=张三丰person.hobby=旅游,美食,音乐person.family.father=张云光person.family.mother=吴文燕person.family.grandpa=张宏宇person.famliy.grandma=唐雨欣person.family.son=张君宝person.family.daughter=张晓敏person.pet.type=泰迪犬person.pet.name=瑞瑞
(4)给Person类添加注解
添加注解@Component,交给Spring去管理
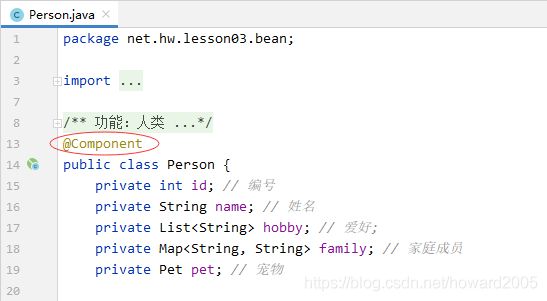
添加注解@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person”)
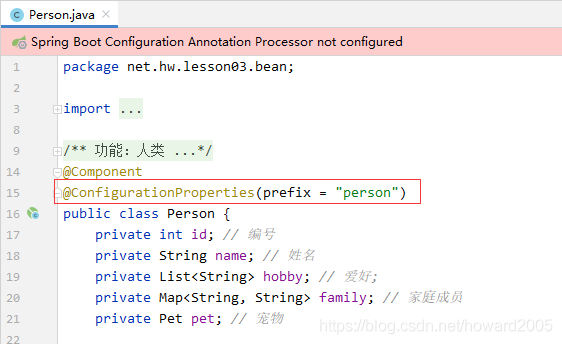
注意:采用@ConfigurationProperties注解方式,必须要有set方法,才会自动为Person类所有属性注入相应的值,包括简单类型和复杂类型
(5)给Pet类添加注解
添加注解@Component,交给Spring去管理 添加注解@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person.pet”) - 可以不用添加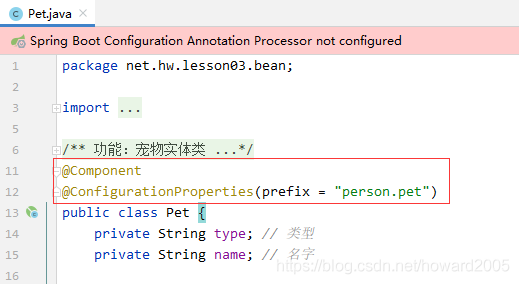
(6)从Spring容器里获取Person类的实例并输出
实现接口ApplicationContextAware,实现其抽象方法setApplicationContext
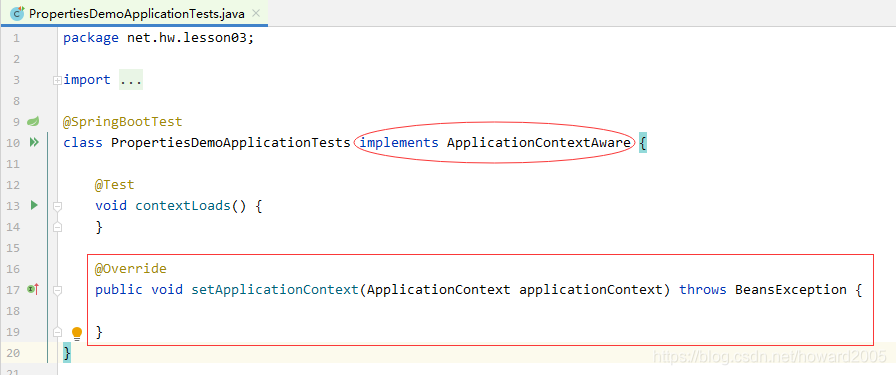
声明ApplicationContext对象,并在setApplicationContext里初始化
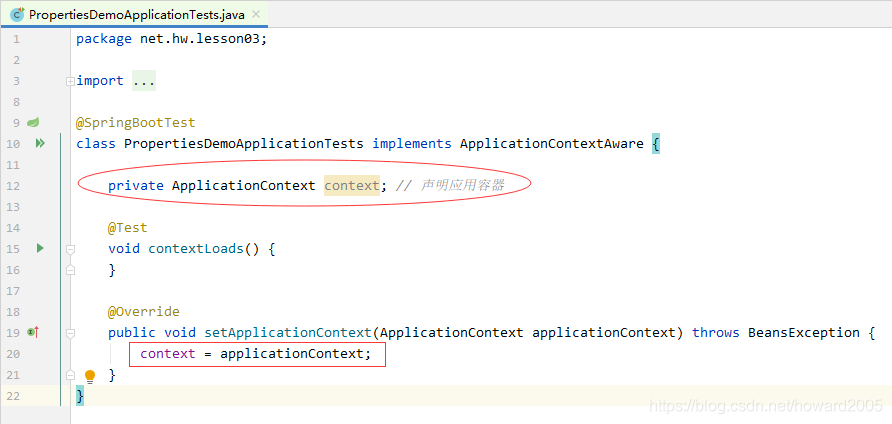
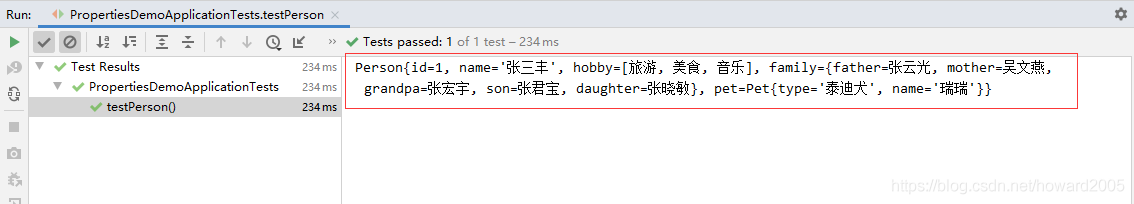
创建测试方法testPerson(),从Spring容器中获取Person类的实例并输出
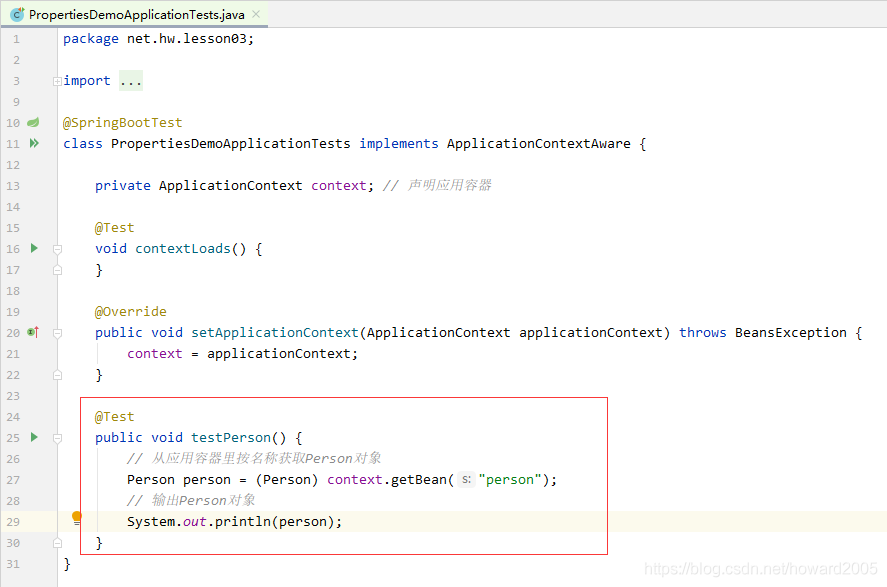
运行测试方法testPerson(),查看结果
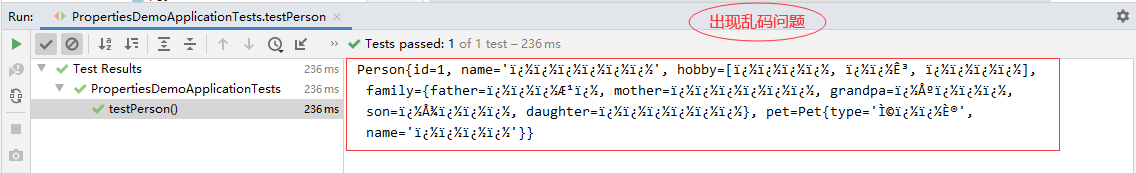
(7)解决输出结果的汉字乱码问题
使用JDK工具native2ascii.exe将汉字处理成uncode编码
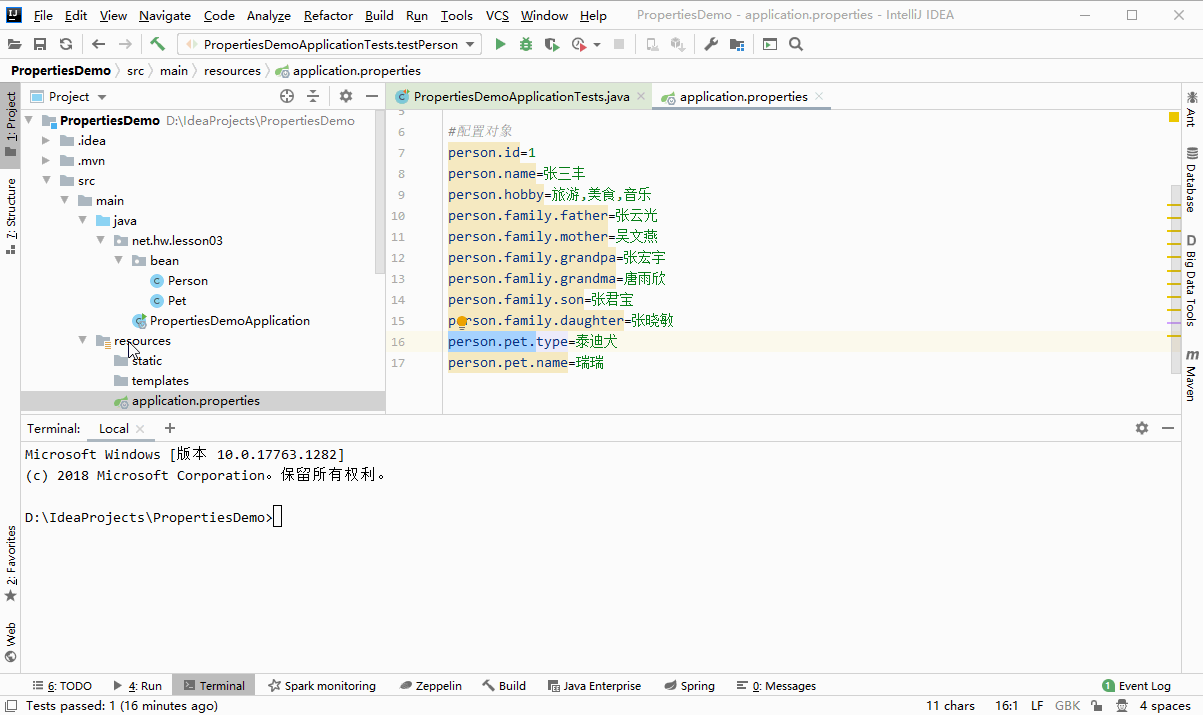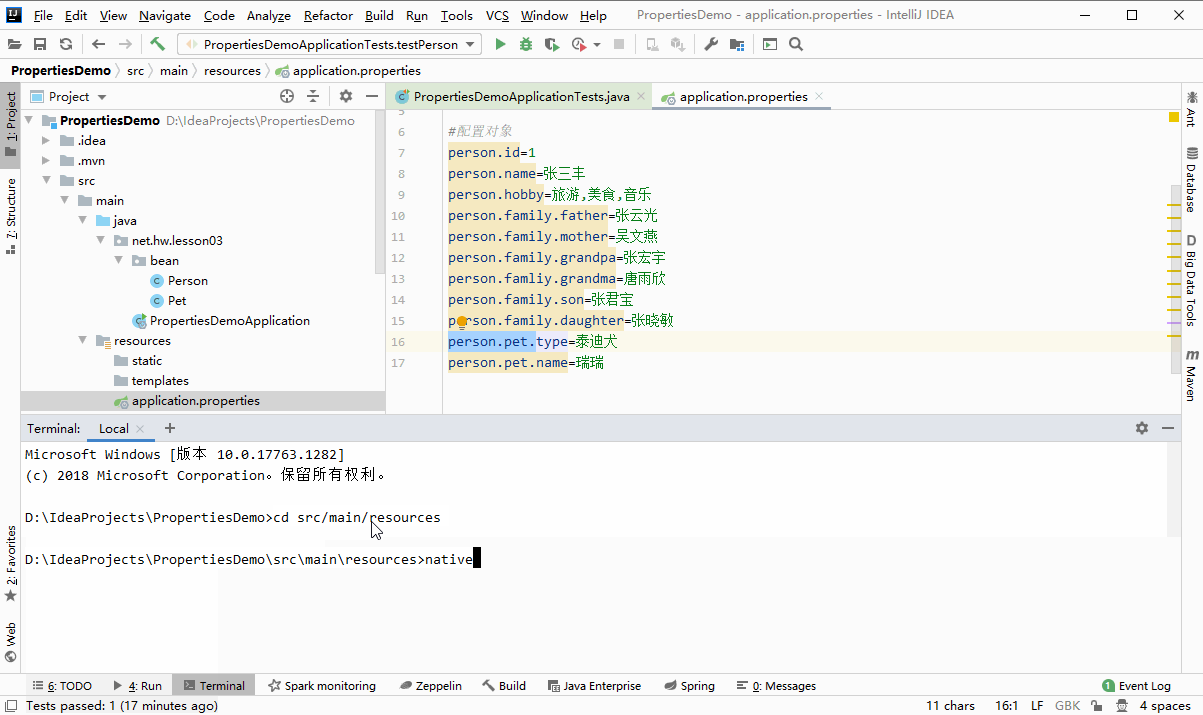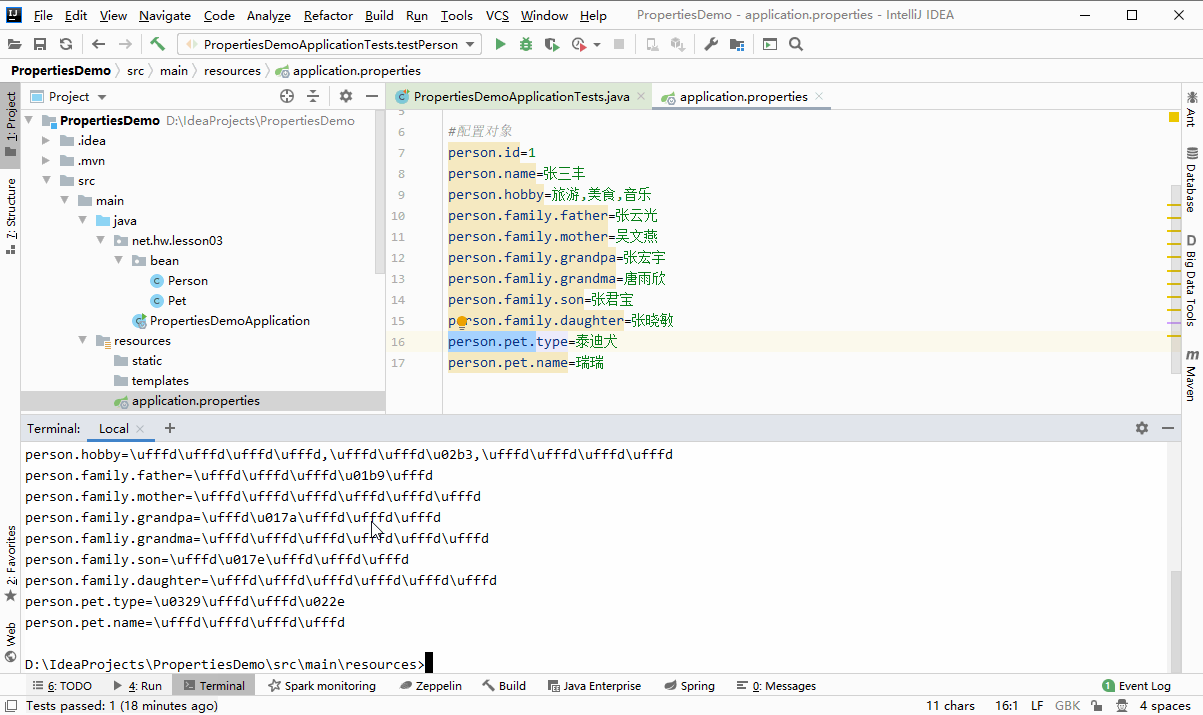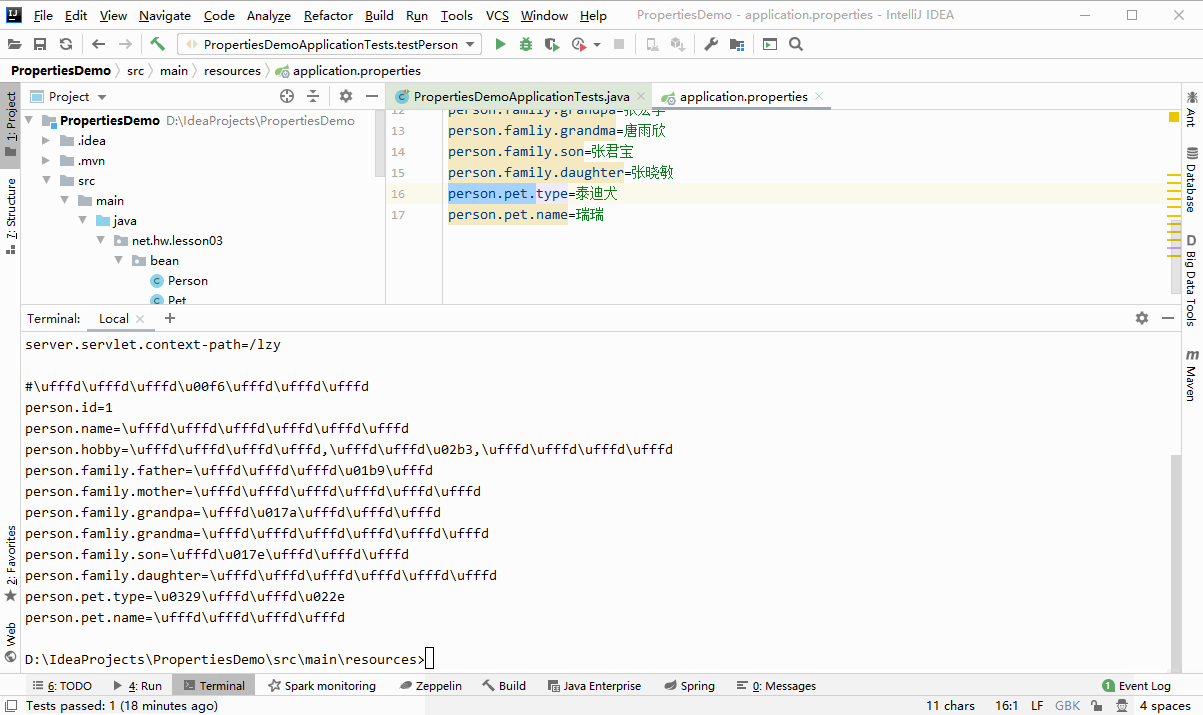
D:IdeaProjectsPropertiesDemo>cd src/main/resources D:IdeaProjectsPropertiesDemosrcmainresources>native2ascii -encoding utf8 application.properties#u4feeu6539tomcatu9ed8u8ba4u7aefu53e3u53f7server.port=8888#u4feeu6539webu865au62dfu8defu5f84server.servlet.context-path=/lzy #u914du7f6eu5bf9u8c61person.id=1person.name=u5f20u4e09u4e30person.hobby=u65c5u6e38,u7f8eu98df,u97f3u4e50person.family.father=u5f20u4e91u5149person.family.mother=u5434u6587u71d5person.family.grandpa=u5f20u5b8fu5b87person.famliy.grandma=u5510u96e8u6b23person.family.son=u5f20u541bu5b9dperson.family.daughter=u5f20u6653u654fperson.pet.type=u6cf0u8feau72acperson.pet.name=u745eu745e D:IdeaProjectsPropertiesDemosrcmainresources>
修改application.properties文件,汉字采用unicode编码形式
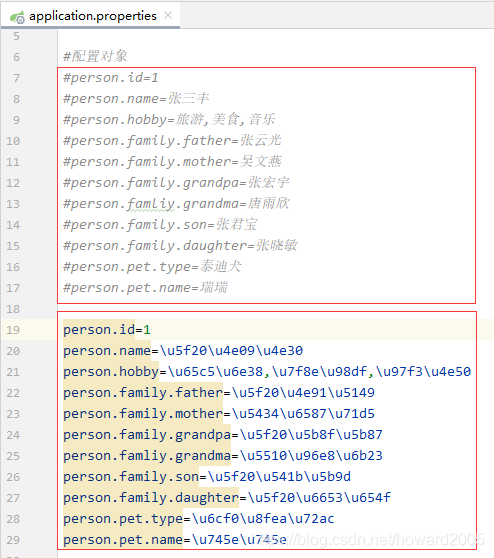
运行测试方法testPerson(),查看结果
(8)从Spring容器里获取Pet类的实例并输出
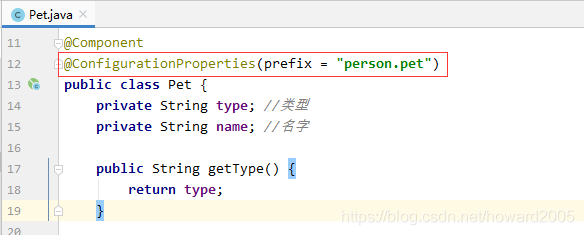
查看Pet类的注解,有配置属性的注解@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = 'person.pet')
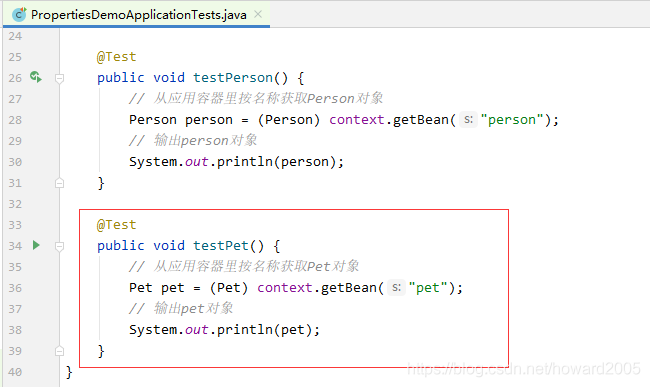
在测试类里添加测试方法testPet()
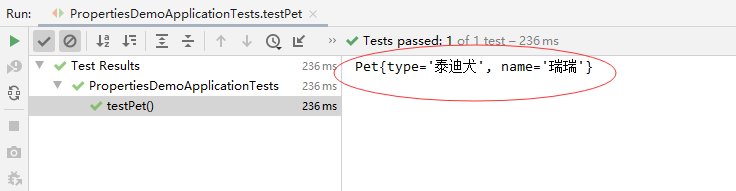
运行测试方法testPet(),查看结果
注释掉Pet类的配置属性的注解@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = 'person.pet')
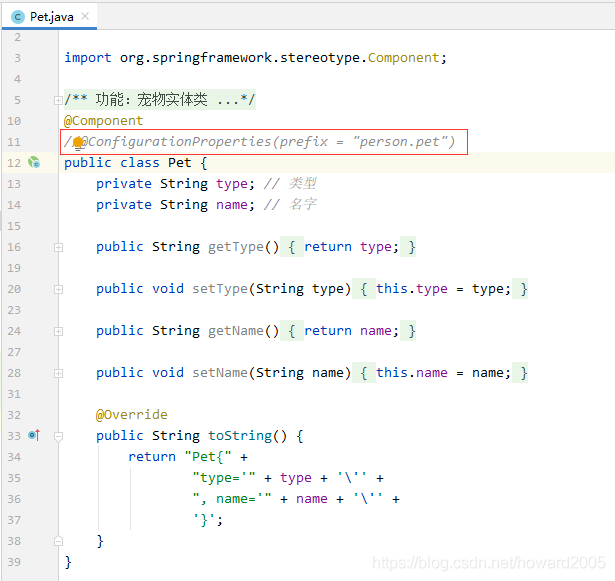
再次运行测试方法testPet(),查看结果
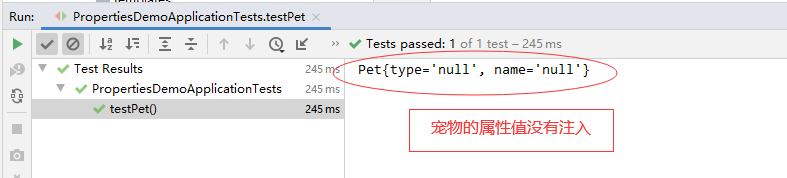
修改application.properties,配置宠物对象
再次运行测试方法testPet(),查看结果
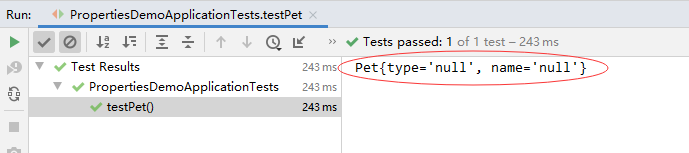
大家可以看到,宠物对象的属性依然没有被注入,下面我们换一种属性注解的方式,采用@Value注解方式。
给Pet类的属性添加值注解@Value
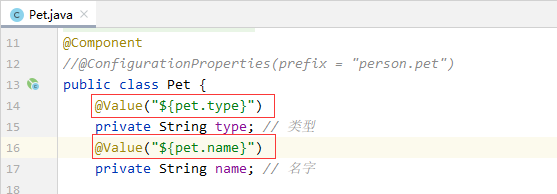
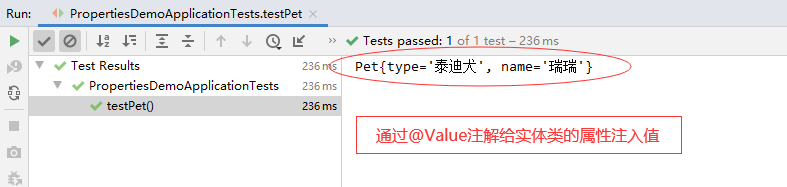
再次运行测试方法testPet(),查看结果
1、备份application.properties文件 文件更名为application.back,即让此文件不起作用
2、在resoures目录里创建application.yaml文件
创建application.yaml文件
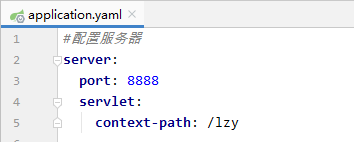
配置服务器属性
配置person对象属性

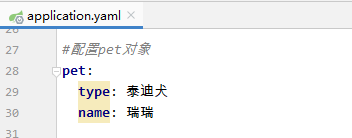
配置pet对象属性
查看application.yaml文件内容
#配置服务器server: port: 8888 servlet: context-path: /lzy #配置person对象person: id: 1 name: 张三丰 hobby: 旅游 美食 音乐 family: { father: 张云光, mother: 吴文燕, grandpa: 张宏宇, grandma: 唐雨欣, son: 张君宝, daughter: 张晓敏 } pet: type: 泰迪犬 name: 瑞瑞 #配置pet对象pet: type: 泰迪犬 name: 瑞瑞
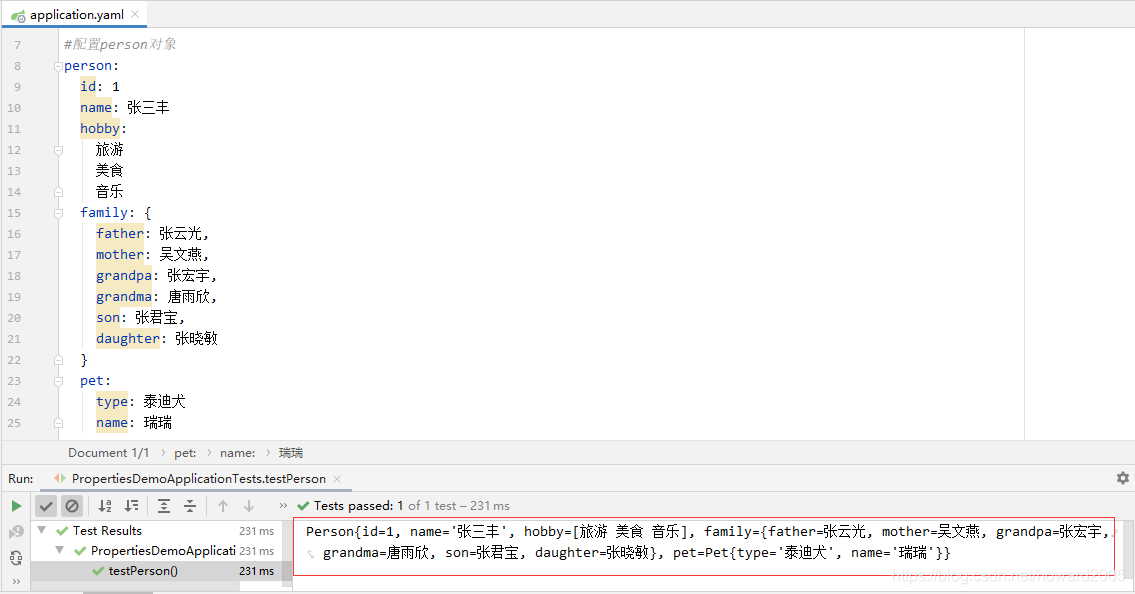
3、运行测试方法testPerson(),查看结果
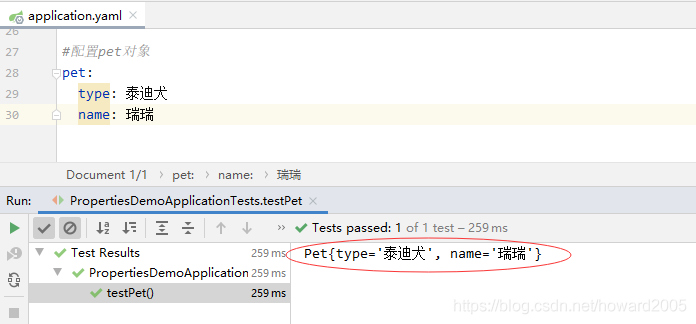
4、运行测试方法testPet(),查看结果
1、application.properties配置文件
采用XML语法,键值对:键=值,没有层次结构 如果值里有汉字,必须得转成unicode,否则会出现乱码问题2、application.yaml配置文件
采用YAML语法,键值对:键: 值(冒号与值之间有空格),具有层次结构 允许值里有汉字,不必转成unicode,也不会出现乱码问题五、课后作业任务:修改StudentInfo项目输出学生信息
创建学生实体类Student
添加属性
private String id;private String name;private String gender;private int age;private String major;private String telephone;private String email;private String hobby; 添加getter和setter 添加toString()方法 添加注解@Component 添加注解@ConfigureProperties 将application.properties更名为application.yaml
配置student对象属性

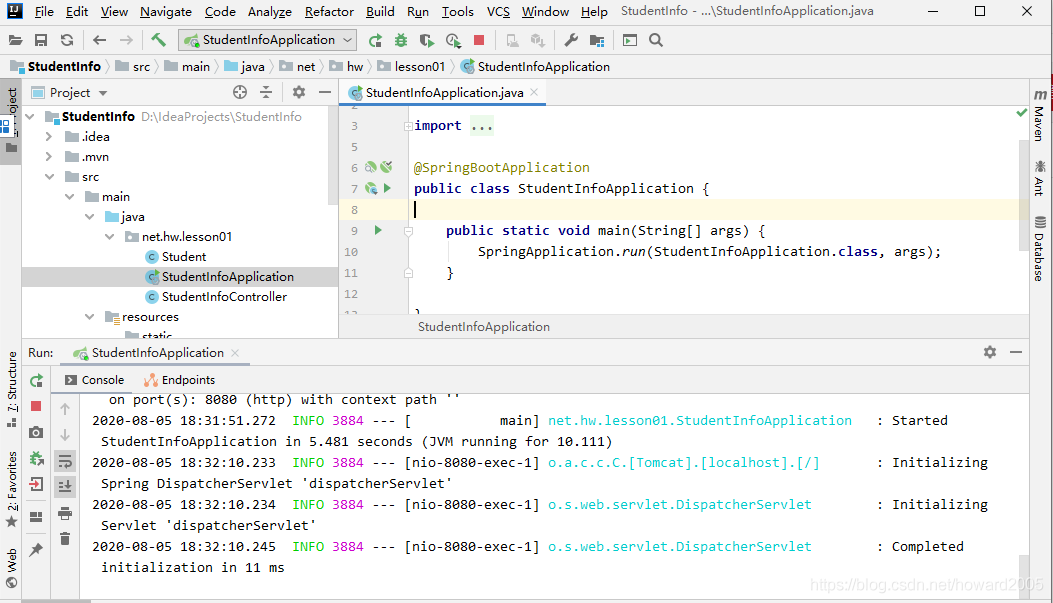
在浏览器里访问http://localhost:8080/student

到此这篇关于Spring Boot两种全局配置和两种注解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Spring Boot配置注解内容请搜索好吧啦网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦网!
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备