Spring使用AspectJ的注解式实现AOP面向切面编程
AOP:面向切面编程,相对于OOP面向对象编程。
Spring的AOP的存在目的是为了解耦。AOP可以让一组类共享相同的行为。在OOP中只能通过继承类和实现接口,来使代码的耦合度增强,而且类的继承只能为单继承,阻碍更多行为添加到一组类上,AOP弥补了OOP的不足。
1.2 AOP中的概念 切入点(pointcut): 切入点(pointcut):在哪些类、哪些方法上切入。 通知(advice):在方法前、方法后、方法前后做什么。 切面(aspect):切面 = 切入点 + 通知。即在什么时机、什么地方、做什么。 织入(weaving):把切面加入对象,并创建出代理对象的过程。 环绕通知:AOP中最强大、灵活的通知,它继承了前置和后置通知,保留了连接点原有的方法。2、认识AspectJ 2.1 AspectJ的简介AspectJ是一个面向切面编程的框架,它扩展了Java语言。AspectJ定义了AOP语法,它有一个专门的编译器用来生成遵守Java字节编码规范的Class文件。AspectJ还支持原生的Java,只需要加上AspectJ提供的注解即可。
2.2 Spring AOP 和 AspectJ比较简单地说,Spring AOP 和 AspectJ 有不同的目标。
Spring AOP 旨在提供一个跨 Spring IoC 的简单的 AOP 实现,以解决程序员面临的最常见问题。它不打算作为一个完整的 AOP 解决方案 —— 它只能应用于由 Spring 容器管理的 Bean。
AspectJ 是原始的 AOP 技术,目的是提供完整的 AOP 解决方案。它更健壮,但也比 Spring AOP 复杂得多。还值得注意的是,AspectJ 可以在所有域对象中应用。
2.3 Spring支持AspectJ的注解式切面编程(1)使用@Aspect声明一个切面。
(2)使用@After、@Before、@Around定义建言(advice),可直接将拦截规则(切点)作为参数。
(3)其中@After、@Before、@Around参数的拦截规则为切点(PointCut),为了使切点复用,可以使用@Pointcut专门定义拦截规则,然后在@After、@Before、@Around的参数中调用。
(4)其中符合条件的每一个被拦截处为连接点(JoinPoint)。
拦截方式分为:基于注解式拦截、基于方法规则式拦截。
其中注解式拦截能够很好地控制要拦截的粒度和获得更丰富的信息,Spring本身在事务处理(@Transactional)和数据缓存(@Cacheable)等都使用了基于注解式拦截。
2.4 AspectJ的注解说明 @Aspect:标记为切面类。 @Before:在切入点开始处切入内容。 @After:在切入点结尾处切入内容。 @AfterReturning:在切入点return内容之后切入内容(可以用来对处理返回值做一些加工处理)。 @Around:在切入点前后切入内容,并自己控制何时执行切入点自身的内容。 @AfterThrowing:用来处理当切入内容部分抛出异常之后的处理逻辑。3、Spring使用AspectJ实现日志记录操作【实例】使用基于注解式拦截和基于方法规则式拦截两种方式,实现模拟日志记录操作。
(1)添加相关的jar包添加SpringAOP支持及AspectJ依赖,pom.xml文件的配置如下:
<properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <spring.version>5.2.3.RELEASE</spring.version> <aspectj.version>1.9.5</aspectj.version></properties> <dependencies> <!-- Spring框架 --> <dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-core</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-context</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency><groupId>org.springframework</groupId><artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId><version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <!-- Aspectj依赖 --> <dependency><groupId>org.aspectj</groupId><artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId><version>${aspectj.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency><groupId>org.aspectj</groupId><artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId><version>${aspectj.version}</version> </dependency></dependencies>(2)编写拦截规则的注解
package com.pjb.aop;import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;import java.lang.annotation.Target;/** * 日志记录注解 * @author pan_junbiao **/@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface LogAction{ String name();}(3)编写使用注解的被拦截类
package com.pjb.aop;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;/** * 使用注解的被拦截类 * @author pan_junbiao **/@Servicepublic class DemoAnnotationService{ @LogAction(name='注解式拦截的add操作') public void add() {System.out.println('执行新增操作'); }}(4)编写使用方法规则的被拦截类
package com.pjb.aop;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;/** * 使用方法规则被拦截类 * @author pan_junbiao **/@Servicepublic class DemoMethodService{ public void add() {System.out.println('执行新增操作'); }}(5)编写切面
package com.pjb.aop;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.lang.reflect.Method;/** * 切面 * @author pan_junbiao * 说明: * 通过@Aspect注解声明一个切面 * 通过@Component注解让此切面成为Spring容器管理的Bean **/@Aspect@Componentpublic class LogAspect{ /** * 通过@Pointcut注解声明切点 */ @Pointcut('@annotation(com.pjb.aop.LogAction)') public void annotationPointCut(){}; /** * 通过@After注解声明一个建言,并使用@Pointcut注解定义的切点 */ @After('annotationPointCut()') public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint) {MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature();Method method = signature.getMethod();LogAction logAction = method.getAnnotation(LogAction.class);//通过反射获取注解上的属性,然后做日志记录的相关操System.out.println('[日志记录]注解式拦截,'+logAction.name()); } /** * 通过@Before注解声明一个建言,此建言直接使用拦截规则作为参数 */ @Before('execution(* com.pjb.aop.DemoMethodService.*(..))') public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature)joinPoint.getSignature();Method method = signature.getMethod();System.out.println('[日志记录]方法规则式拦截,'+method.getName()); }}(6)配置类
package com.pjb.aop;import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;/** * 配置类 * @author pan_junbiao * 说明: * 使用@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解开启Spring对AspectJ的支持 **/@Configuration@ComponentScan('com.pjb.aop')@EnableAspectJAutoProxypublic class AopConfig{}(7)运行
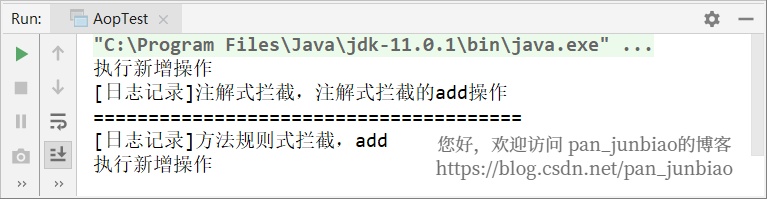
package com.pjb.aop;import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;/** * 测试类 * @author pan_junbiao **/public class AopTest{ public static void main(String[] args) {AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AopConfig.class);DemoAnnotationService demoAnnotationService = context.getBean(DemoAnnotationService.class);DemoMethodService demoMethodService = context.getBean(DemoMethodService.class); demoAnnotationService.add();System.out.println('=======================================');demoMethodService.add(); context.close(); }}
执行结果:
【示例】SpringBoot项目中使用AspectJ实现日志记录操作。
(1)pom.xml文件的配置<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId></dependency>(2)编写AOP日志注解类
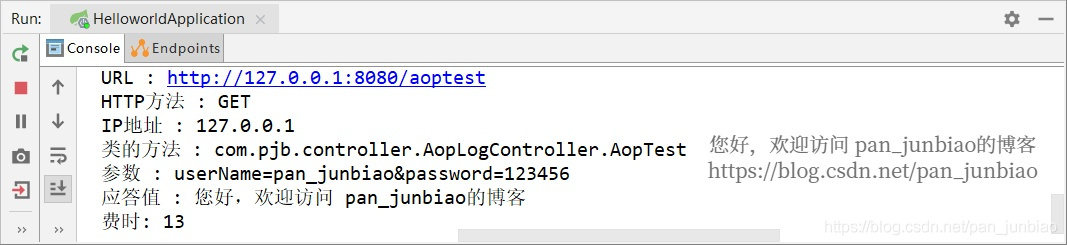
package com.pjb.aop;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; /** * AOP管理日志 * @author pan_junbiao **/@Aspect@Componentpublic class AopLog{ private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass()); //线程局部的变量,用于解决多线程中相同变量的访问冲突问题 ThreadLocal<Long> startTime = new ThreadLocal<>(); //定义切点 @Pointcut('execution(public * com.pjb..*.*(..))') public void aopWebLog() { } //使用@Before在切入点开始处切入内容 @Before('aopWebLog()') public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {startTime.set(System.currentTimeMillis());// 接收到请求,记录请求内容ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest(); // 记录下请求内容logger.info('URL : ' + request.getRequestURL().toString());logger.info('HTTP方法 : ' + request.getMethod());logger.info('IP地址 : ' + request.getRemoteAddr());logger.info('类的方法 : ' + joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() + '.' + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());//logger.info('参数 : ' + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));logger.info('参数 : ' + request.getQueryString()); } //使用@AfterReturning在切入点return内容之后切入内容(可以用来对处理返回值做一些加工处理) @AfterReturning(pointcut = 'aopWebLog()',returning = 'retObject') public void doAfterReturning(Object retObject) throws Throwable {// 处理完请求,返回内容logger.info('应答值 : ' + retObject);logger.info('费时: ' + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime.get())); } //使用@AfterThrowing用来处理当切入内容部分抛出异常之后的处理逻辑 //抛出异常后通知(After throwing advice) : 在方法抛出异常退出时执行的通知。 @AfterThrowing(pointcut = 'aopWebLog()', throwing = 'ex') public void addAfterThrowingLogger(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception ex) {logger.error('执行 ' + ' 异常', ex); }}(3)编写控制器用于测试
下面的控制器构造了一个普通的Rest风格的页面。
package com.pjb.controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;/** * 日志控制器 * @author pan_junbiao **/@RestControllerpublic class AopLogController{ @GetMapping('/aoptest') public String AopTest(String userName,String password) {return '您好,欢迎访问 pan_junbiao的博客'; }}(4)运行
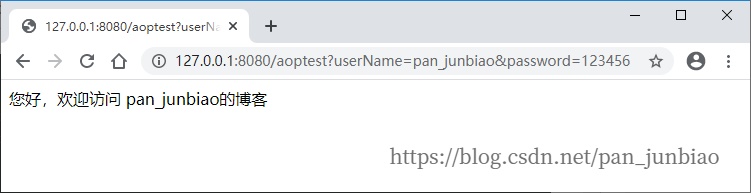
启动项目,在浏览器中访问 “http://127.0.0.1:8080/aoptest?userName=pan_junbiao&password=123456”
浏览器执行结果:
控制台输出结果:
网上大多数介绍AspectJ的文章都是和Spring容器混用的,但有时我们想自己写框架就需要抛开Spring造轮子,类似使用原生AspectJ达到面向切面编程。步骤很简单,只需要两步。
1.导入依赖<dependency> <groupId>org.aspectj</groupId> <artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId> <version>1.9.3</version></dependency>2.Maven插件
<plugin> <groupId>org.codehaus.mojo</groupId> <artifactId>aspectj-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>1.10</version> <configuration><source>1.8</source><target>1.8</target><complianceLevel>1.8</complianceLevel> </configuration> <executions><execution> <goals><goal>compile</goal> </goals></execution> </executions></plugin>3.使用注解
@Aspectpublic class AspectDemo { @Pointcut('execution(* cn.yueshutong.App.say())') private void pointcut() {} // signature @Before('pointcut()') public void before(){System.out.println('Hello'); }}
App.java
public class App { public static void main( String[] args ) {System.out.println( new App().say() ); } public String say() {return 'World'; }}
这一步就和平常使用Spring AOP注解没有什么区别了。
4.织入/代理我们都知道,Spring AOP是通过动态代理生成一个代理类,这种方式的最大缺点就是对于对象内部的方法嵌套调用不会走代理类,比如下面这段代码:
@Componentpublic class TestComponent { @TestAspect public void work(){//do sth } public void call(){work(); }}
原因很简单,对象内部的方法调用该对象的其他方法是通过自身this进行引用,并不是通过代理类引用。而AspectJ则不同,AspectJ是通过织入的方式将切面代码织入进原对象内部,并不会生成额外的代理类。
关于这一点,我们反编译看一下切点代码:
//原方法 public void say() {System.out.println(this.getClass().getName());hi(); } //反编译 public void say() {ResourceAspect.aspectOf().before();System.out.println(this.getClass().getName());this.hi(); }
深究下去,在Spring AOP中,我们只有调用代理类的切点方法才能触发Before方法,因为代理类本质上是对原类的一层封装,原类是没有变化的,原类的方法内部的this指向的依旧是原类,这就导致了原类方法内部的嵌套调用无法被代理类感知到,而AspectJ的织入就不同了,它会动态改变你的原类代码,将Before等方法全部写入进你的原方法中,这就保证了面向切面编程的万无一失。
两种方式,各有利弊,如何使用还需要视情况而行。
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦网。
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备