Django多数据库配置及逆向生成model教程
在项目中我们每个app对应不同的数据库,其中有一个是从数据库逆向生成model,做个笔记。
1、修改项目的setting.py配置 :
DATABASES = { ’default’: { ’ENGINE’: ’django.db.backends.mysql’, # 默认用mysql ’NAME’: ’bk’, # 数据库名 (默认与APP_ID相同) ’USER’: ’root’, # 你的数据库user ’PASSWORD’: ’root’, # 你的数据库password ’HOST’: ’xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx’, # 开发的时候,使用localhost ’PORT’: ’3306’, # 默认3306 }, ’cloudsino_test’: { ’ENGINE’: ’django.db.backends.mysql’, # 默认用mysql ’NAME’: ’cloudsino_test’, # 数据库名 (默认与APP_ID相同) ’USER’: ’root’, # 你的数据库user ’PASSWORD’: ’root’, # 你的数据库password ’HOST’: ’xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx’, # 开发的时候,使用localhost ’PORT’: ’3306’, # 默认3306 },}# 设置数据库的路由规则方法DATABASE_ROUTERS = [’conf.database_router.DatabaseAppsRouter’]# 设置APP对应的数据库路由表,哪个app要连接哪个数据库,没有指定会用default那个。DATABASE_APPS_MAPPING = { # example: #’app_name’:’database_name’, ’home_application’: ’cloudsino_test’, ’cmdb’: ’default’,}
2、新建database_router.py:
在与setting.py文件同级的目录下新建database_router.py文件:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-from settings_development import DATABASE_APPS_MAPPINGDATABASE_MAPPING = DATABASE_APPS_MAPPINGclass DatabaseAppsRouter(object): def db_for_read(self, model, **hints): ''''建议model类型对象从哪一个数据库读取.''' if model._meta.app_label in DATABASE_MAPPING: return DATABASE_MAPPING[model._meta.app_label] return None def db_for_write(self, model, **hints): '''建议model类型对象的写入操作应该使用哪个数据库''' if model._meta.app_label in DATABASE_MAPPING: return DATABASE_MAPPING[model._meta.app_label] return None def allow_relation(self, obj1, obj2, **hints): '''Allow any relation between apps that use the same database. 如果obj1 和obj2 之间应该允许关联则返回True,如果应该防止关联则返回False,如果路由无法判断则返回None ''' db_obj1 = DATABASE_MAPPING.get(obj1._meta.app_label) db_obj2 = DATABASE_MAPPING.get(obj2._meta.app_label) if db_obj1 and db_obj2: if db_obj1 == db_obj2: return True else: return False return None def allow_syncdb(self, db, model): '''Make sure that apps only appear in the related database.''' if db in DATABASE_MAPPING.values(): return DATABASE_MAPPING.get(model._meta.app_label) == db elif model._meta.app_label in DATABASE_MAPPING: return False return None def allow_migrate(self, db, app_label, model=None, **hints): ''' Make sure the auth app only appears in the ’auth_db’ database. 定义迁移操作是否允许在别名为db的数据库上运行。如果操作应该运行则返回True ,如果不应该运行则返回False,如果路由无法判断则返回None。 ''' if db in DATABASE_MAPPING.values(): return DATABASE_MAPPING.get(app_label) == db elif app_label in DATABASE_MAPPING: return False return None
3.逆向生成model:
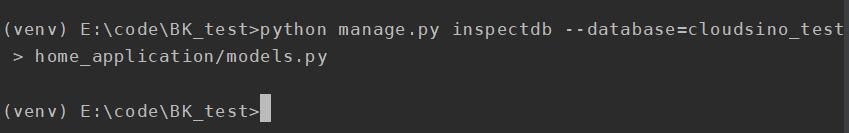
在terminal中输入以下命令,使用名为cloudsino_test的DATABASE来逆向生成model到home_application这个app的models.py:
python manage.py inspectdb --database=cloudsino_test > home_application/models.py
逆向生成的model:
# This is an auto-generated Django model module.# You’ll have to do the following manually to clean this up:# * Rearrange models’ order# * Make sure each model has one field with primary_key=True# * Remove `managed = False` lines if you wish to allow Django to create, modify, and delete the table# Feel free to rename the models, but don’t rename db_table values or field names.## Also note: You’ll have to insert the output of ’django-admin sqlcustom [app_label]’# into your database.from __future__ import unicode_literalsfrom django.db import modelsclass CloudsinoCpuinfo(models.Model): corenumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) frequency = models.CharField(max_length=128) index = models.CharField(max_length=128) manufacturer = models.CharField(max_length=128) name = models.CharField(max_length=128) partnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) serialnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) type = models.CharField(max_length=128) device = models.ForeignKey(’CloudsinoDevice’, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_cpuinfo’class CloudsinoDevice(models.Model): sn = models.CharField(max_length=128) app = models.CharField(max_length=128) business_chargeby1 = models.CharField(max_length=128) business_chargeby2 = models.CharField(max_length=128) chargeby1 = models.CharField(max_length=128) chargeby2 = models.CharField(max_length=128) description = models.CharField(max_length=128) device_status = models.CharField(max_length=128) devicename = models.CharField(max_length=128) field1 = models.CharField(max_length=128) field2 = models.CharField(max_length=128) field3 = models.CharField(max_length=128) field4 = models.CharField(max_length=128) field5 = models.CharField(max_length=128) frame_posiniton = models.CharField(max_length=128) framename = models.CharField(max_length=128) ip = models.CharField(max_length=128) manufacturer = models.CharField(max_length=128) model = models.CharField(max_length=128) os = models.CharField(max_length=128) position_desc = models.CharField(max_length=128) roomarea = models.CharField(max_length=128) roomname = models.CharField(max_length=128) servicetag = models.CharField(max_length=128) shape = models.CharField(max_length=128) specification = models.CharField(max_length=128) subtype = models.CharField(max_length=128) type = models.CharField(max_length=128) ucount = models.CharField(max_length=128) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_device’class CloudsinoDevicetype(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=128) type = models.CharField(max_length=128) status = models.CharField(max_length=128) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_devicetype’class CloudsinoDiskinfo(models.Model): bus = models.CharField(max_length=128) formfactor = models.CharField(max_length=128) index = models.CharField(max_length=128) manufacturer = models.CharField(max_length=128) media = models.CharField(max_length=128) name = models.CharField(max_length=128) partnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) serialnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) size = models.CharField(max_length=128) speed = models.CharField(max_length=128) type = models.CharField(max_length=128) device = models.ForeignKey(CloudsinoDevice, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_diskinfo’class CloudsinoFaninfo(models.Model): index = models.CharField(max_length=128) name = models.CharField(max_length=128) partnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) serialnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) device = models.ForeignKey(CloudsinoDevice, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_faninfo’class CloudsinoHbacardinfo(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=128) wwnn = models.CharField(max_length=128) wwpn = models.CharField(max_length=128) fc_switch = models.CharField(max_length=128) switch_port = models.CharField(max_length=128) switch_mac = models.CharField(max_length=128) device = models.ForeignKey(CloudsinoDevice, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_hbacardinfo’class CloudsinoManageinfo(models.Model): assetcode = models.CharField(max_length=128) department = models.CharField(max_length=128) express_code = models.CharField(max_length=128) service_level = models.CharField(max_length=128) shutdown_level = models.CharField(max_length=128) usage = models.CharField(max_length=128) device = models.ForeignKey(CloudsinoDevice, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_manageinfo’class CloudsinoManufacturertype(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=128) type = models.CharField(max_length=128) status = models.CharField(max_length=128) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_manufacturertype’class CloudsinoMemory(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=128) type = models.CharField(max_length=128) frequency = models.CharField(max_length=128) size = models.CharField(max_length=128) manufacturer = models.CharField(max_length=128) partnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) serialnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) index = models.CharField(max_length=128) memoryinfo = models.ForeignKey(’CloudsinoMemoryinfo’, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_memory’class CloudsinoMemoryinfo(models.Model): max_dimmslots = models.CharField(max_length=128) mem_totalsize = models.CharField(max_length=128) memmax_capacitysize = models.CharField(max_length=128) populated_dimmslots = models.CharField(max_length=128) device = models.ForeignKey(CloudsinoDevice, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_memoryinfo’class CloudsinoNetworkinfo(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=128) type = models.CharField(max_length=128) mac = models.CharField(max_length=128) speed = models.CharField(max_length=128) manufacturer = models.CharField(max_length=128) partnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) serialnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) index = models.CharField(max_length=128) device = models.ForeignKey(CloudsinoDevice, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_networkinfo’class CloudsinoOobnetwork(models.Model): ip = models.CharField(max_length=128) netmask = models.CharField(max_length=128) gateway = models.CharField(max_length=128) mac = models.CharField(max_length=128) ethernet_switch = models.CharField(max_length=128) swith_port = models.CharField(max_length=128) swith_mac = models.CharField(max_length=128) distribution_frame = models.CharField(max_length=128) distribution = models.CharField(max_length=128) device = models.ForeignKey(CloudsinoDevice, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_oobnetwork’class CloudsinoPciecard(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=128) type = models.CharField(max_length=128) loc = models.CharField(max_length=128) online_state = models.CharField(max_length=128) conntype = models.CharField(max_length=128) bandwidth = models.CharField(max_length=128) speed = models.CharField(max_length=128) manufacturer = models.CharField(max_length=128) partnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) serialnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) index = models.CharField(max_length=128) device = models.ForeignKey(CloudsinoDevice, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_pciecard’class CloudsinoPowerinfo(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=128) type = models.CharField(max_length=128) model = models.CharField(max_length=128) outputpower = models.CharField(max_length=128) manufacturer = models.CharField(max_length=128) partnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) serialnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) index = models.CharField(max_length=128) device = models.ForeignKey(CloudsinoDevice, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_powerinfo’class CloudsinoProductnetwork(models.Model): ip = models.CharField(max_length=128) netmask = models.CharField(max_length=128) gateway = models.CharField(max_length=128) mac = models.CharField(max_length=128) os = models.CharField(max_length=128) remote_type = models.CharField(max_length=128) remote_port = models.CharField(max_length=128) ethernet_switch = models.CharField(max_length=128) swith_port = models.CharField(max_length=128) swith_mac = models.CharField(max_length=128) distribution_frame = models.CharField(max_length=128) distribution = models.CharField(max_length=128) device = models.ForeignKey(CloudsinoDevice, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_productnetwork’class CloudsinoPurchasewarrantyinfo(models.Model): date_manuf = models.CharField(max_length=128) expiredate = models.CharField(max_length=128) price = models.CharField(max_length=128) purchase_order = models.CharField(max_length=128) purchase_order_name = models.CharField(max_length=128) purchase_supply = models.CharField(max_length=128) serviceagent = models.CharField(max_length=128) warrantyitem = models.CharField(db_column=’warrantyItem’, max_length=128) # Field name made lowercase. warrantyperiod = models.CharField(db_column=’warrantyPeriod’, max_length=128) # Field name made lowercase. warrantystartdate = models.CharField(db_column=’warrantyStartDate’, max_length=128) # Field name made lowercase. warrantytype = models.CharField(db_column=’warrantyType’, max_length=128) # Field name made lowercase. device = models.ForeignKey(CloudsinoDevice, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_purchasewarrantyinfo’class CloudsinoRaidinfo(models.Model): name = models.CharField(max_length=128) type = models.CharField(max_length=128) cachesize = models.CharField(max_length=128) speed = models.CharField(max_length=128) manufacturer = models.CharField(max_length=128) partnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) serialnumber = models.CharField(max_length=128) index = models.CharField(max_length=128) device = models.ForeignKey(CloudsinoDevice, blank=True, null=True) class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’cloudsino_raidinfo’class DjangoMigrations(models.Model): app = models.CharField(max_length=255) name = models.CharField(max_length=255) applied = models.DateTimeField() class Meta: managed = False db_table = ’django_migrations’
补充知识:Django使用数据库生成模型类
正常的开发流程
在models.py中定义模型类,要求继承自models.Model
把应用加入settings.py文件的installed_app项
生成迁移文件
执行迁移生成表
使用模型类进行crud操作
使用数据库生成模型类
python manage.py inspectdb > app_name/models.py
例如:
python manage.py inspectdb > booktest/models.py
以上这篇Django多数据库配置及逆向生成model教程就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦网。
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备