浅析Python实现DFA算法
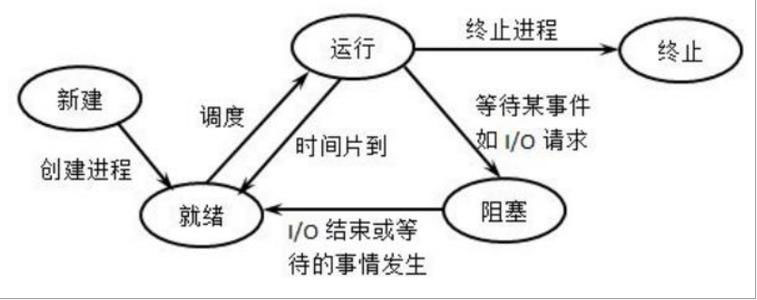
计算机操作系统中的进程状态与切换可以作为 DFA 算法的一种近似理解。如下图所示,其中椭圆表示状态,状态之间的连线表示事件,进程的状态以及事件都是可确定的,且都可以穷举。
DFA 算法具有多种应用,在此先介绍在匹配关键词领域的应用。
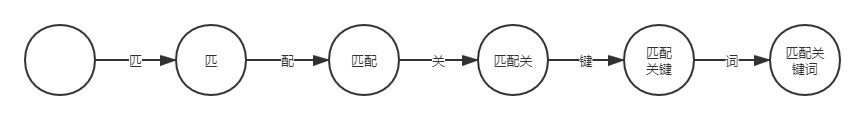
二、匹配关键词我们可以将每个文本片段作为状态,例如“匹配关键词”可拆分为“匹”、“匹配”、“匹配关”、“匹配关键”和“匹配关键词”五个文本片段。
【过程】:
初始状态为空,当触发事件“匹”时转换到状态“匹”; 触发事件“配”,转换到状态“匹配”; 依次类推,直到转换为最后一个状态“匹配关键词”。再让我们考虑多个关键词的情况,例如“匹配算法”、“匹配关键词”以及“信息抽取”。
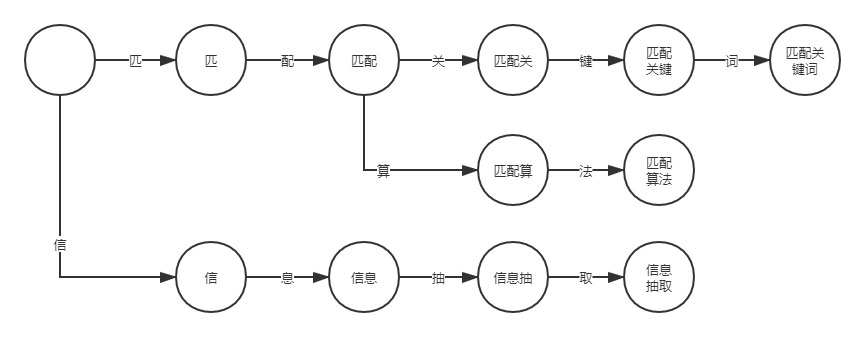
可以看到上图的状态图类似树形结构,也正是因为这个结构,使得 DFA 算法在关键词匹配方面要快于关键词迭代方法(for 循环)。经常刷 LeetCode 的读者应该清楚树形结构的时间复杂度要小于 for 循环的时间复杂度。
for 循环:
keyword_list = []for keyword in ['匹配算法', '匹配关键词', '信息抽取']: if keyword in 'DFA 算法匹配关键词':keyword_list.append(keyword)
for 循环需要遍历一遍关键词表,随着关键词表的扩充,所需的时间也会越来越长。
DFA 算法:找到“匹”时,只会按照事件走向特定的序列,例如“匹配关键词”,而不会走向“匹配算法”,因此遍历的次数要小于 for 循环。具体的实现放在下文中。
【问】:那么如何构建状态图所示的结构呢?
【答】:在 Python 中我们可以使用 dict 数据结构。
state_event_dict = { '匹': {'配': { '算': {'法': { 'is_end': True},'is_end': False }, '关': {'键': { '词': {'is_end': True }, 'is_end': False},'is_end': False }, 'is_end': False},'is_end': False }, '信': {'息': { '抽': {'取': { 'is_end': True},'is_end': False }, 'is_end': False},'is_end': False }}
用嵌套字典来作为树形结构,key 作为事件,通过 is_end 字段来判断状态是否为最后一个状态,如果是最后一个状态,则停止状态转换,获取匹配的关键词。
【问】:如果关键词存在包含关系,例如“匹配关键词”和“匹配”,那么该如何处理呢?
【答】:我们仍然可以用 is_end 字段来表示关键词的结尾,同时添加一个新的字段,例如 is_continue 来表明仍可继续进行匹配。除此之外,也可以通过寻找除 is_end 字段外是否还有其他的字段来判断是否继续进行匹配。例如下面代码中的“配”,除了 is_end 字段外还有“关”,因此还需要继续进行匹配。
state_event_dict = { '匹': {'配': { '关': {'键': { '词': {'is_end': True }, 'is_end': False},'is_end': False }, 'is_end': True},'is_end': False }}
接下来,我们来实现这个算法。
三、算法实现使用 Python 3.6 版本实现,当然 Python 3.X 都能运行。
3.1、构建存储结构def _generate_state_event_dict(keyword_list: list) -> dict: state_event_dict = {} # 遍历每一个关键词 for keyword in keyword_list:current_dict = state_event_dictlength = len(keyword)for index, char in enumerate(keyword): if char not in current_dict:next_dict = {'is_end': False}current_dict[char] = next_dictcurrent_dict = next_dict else:next_dict = current_dict[char]current_dict = next_dict if index == length - 1:current_dict['is_end'] = True return state_event_dict
关于上述代码仍然有不少可迭代优化的地方,例如先对关键词列表按照字典序进行排序,这样可以让具有相同前缀的关键词集中在一块,从而在构建存储结构时能够减少遍历的次数。
3.2、匹配关键词def match(state_event_dict: dict, content: str): match_list = [] state_list = [] temp_match_list = [] for char_pos, char in enumerate(content):# 首先找到匹配项的起点if char in state_event_dict: state_list.append(state_event_dict) temp_match_list.append({'start': char_pos,'match': '' })# 可能会同时满足多个匹配项,因此遍历这些匹配项for index, state in enumerate(state_list): if char in state:state_list[index] = state[char]temp_match_list[index]['match'] += char# 如果抵达匹配项的结尾,表明匹配关键词完成if state[char]['is_end']: match_list.append(copy.deepcopy(temp_match_list[index])) # 如果还能继续,则继续进行匹配 if len(state[char].keys()) == 1:state_list.pop(index)temp_match_list.pop(index) # 如果不满足匹配项的要求,则将其移除 else:state_list.pop(index)temp_match_list.pop(index) return match_list3.3、完整代码
import reimport copyclass DFA: def __init__(self, keyword_list: list):self.state_event_dict = self._generate_state_event_dict(keyword_list) def match(self, content: str):match_list = []state_list = []temp_match_list = []for char_pos, char in enumerate(content): if char in self.state_event_dict:state_list.append(self.state_event_dict)temp_match_list.append({ 'start': char_pos, 'match': ''}) for index, state in enumerate(state_list):if char in state: state_list[index] = state[char] temp_match_list[index]['match'] += char if state[char]['is_end']:match_list.append(copy.deepcopy(temp_match_list[index]))if len(state[char].keys()) == 1: state_list.pop(index) temp_match_list.pop(index)else: state_list.pop(index) temp_match_list.pop(index)return match_list @staticmethod def _generate_state_event_dict(keyword_list: list) -> dict:state_event_dict = {}for keyword in keyword_list: current_dict = state_event_dict length = len(keyword) for index, char in enumerate(keyword):if char not in current_dict: next_dict = {'is_end': False} current_dict[char] = next_dict current_dict = next_dictelse: next_dict = current_dict[char] current_dict = next_dictif index == length - 1: current_dict['is_end'] = Truereturn state_event_dictif __name__ == '__main__': dfa = DFA(['匹配关键词', '匹配算法', '信息抽取', '匹配']) print(dfa.match('信息抽取之 DFA 算法匹配关键词,匹配算法'))
输出:
[
{
’start’: 0,
’match’: ’信息抽取’
}, {
’start’: 12,
’match’: ’匹配’
}, {
’start’: 12,
’match’: ’匹配关键词’
}, {
’start’: 18,
’match’: ’匹配’
}, {
’start’: 18,
’match’: ’匹配算法’
}
]
四、其他用法4.1、添加通配符在敏感词识别时往往会遇到同一种类型的句式,例如“你这个傻X”,其中 X 可以有很多,难道我们需要一个个添加到关键词表中吗?最好能够通过类似正则表达式的方法去进行识别。一个简单的做法就是“*”,匹配任何内容。
添加通配符只需要对匹配关键词过程进行修改:
def match(self, content: str): match_list = [] state_list = [] temp_match_list = [] for char_pos, char in enumerate(content):if char in self.state_event_dict: state_list.append(self.state_event_dict) temp_match_list.append({'start': char_pos,'match': '' })for index, state in enumerate(state_list): is_find = False state_char = None # 如果是 * 则匹配所有内容 if '*' in state:state_list[index] = state['*']state_char = state['*']is_find = True if char in state:state_list[index] = state[char]state_char = state[char]is_find = True if is_find:temp_match_list[index]['match'] += charif state_char['is_end']: match_list.append(copy.deepcopy(temp_match_list[index])) if len(state_char.keys()) == 1:state_list.pop(index)temp_match_list.pop(index) else:state_list.pop(index)temp_match_list.pop(index) return match_list
main() 函数。
if __name__ == '__main__': dfa = DFA(['匹配关键词', '匹配算法', '信息*取', '匹配']) print(dfa.match('信息抽取之 DFA 算法匹配关键词,匹配算法,信息抓取'))
输出:
[
{
’start’: 0,
’match’: ’信息抽取’
}, {
’start’: 12,
’match’: ’匹配’
}, {
’start’: 12,
’match’: ’匹配关键词’
}, {
’start’: 18,
’match’: ’匹配’
}, {
’start’: 18,
’match’: ’匹配算法’
}, {
’start’: 23,
’match’: ’信息抓取’
}
]
以上就是浅析Python实现DFA算法的详细内容,更多关于Python DFA算法的资料请关注好吧啦网其它相关文章!
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备