Python集成学习之Blending算法详解
普通机器学习:从训练数据中学习一个假设。
集成方法:试图构建一组假设并将它们组合起来,集成学习是一种机器学习范式,多个学习器被训练来解决同一个问题。
集成方法分类为:
Bagging(并行训练):随机森林
Boosting(串行训练):Adaboost; GBDT; XgBoost
Stacking:
Blending:
或者分类为串行集成方法和并行集成方法
1.串行模型:通过基础模型之间的依赖,给错误分类样本一个较大的权重来提升模型的性能。
2.并行模型的原理:利用基础模型的独立性,然后通过平均能够较大地降低误差
二、Blending介绍训练数据划分为训练和验证集+新的训练数据集和新的测试集
将训练数据进行划分,划分之后的训练数据一部分训练基模型,一部分经模型预测后作为新的特征训练元模型。测试数据同样经过基模型预测,形成新的测试数据。最后,元模型对新的测试数据进行预测。Blending框架图如下所示:注意:其是在stacking的基础上加了划分数据
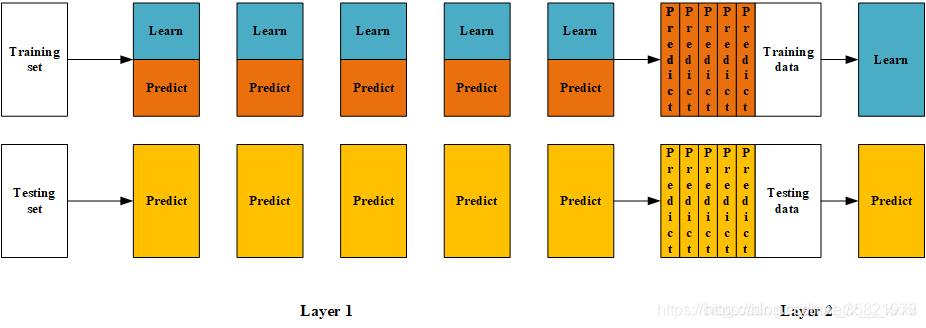
三、Blending流程图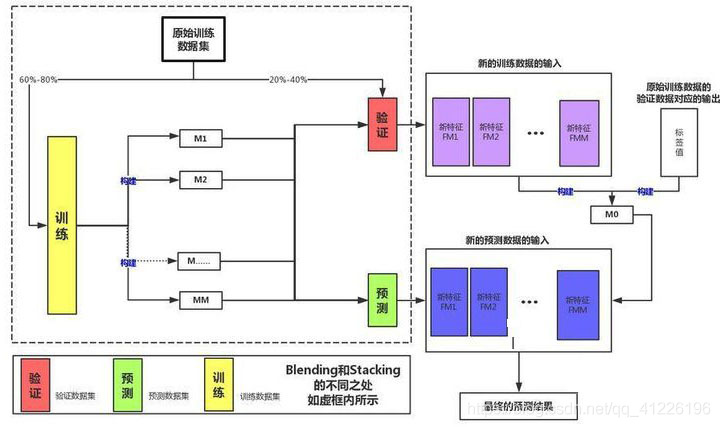
相关工具包加载
import numpy as npimport pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as pltplt.style.use('ggplot')%matplotlib inlineimport seaborn as sns
创建数据
from sklearn import datasets from sklearn.datasets import make_blobsfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitdata, target = make_blobs(n_samples=10000, centers=2, random_state=1, cluster_std=1.0 )## 创建训练集和测试集X_train1,X_test,y_train1,y_test = train_test_split(data, target, test_size=0.2, random_state=1)## 创建训练集和验证集X_train,X_val,y_train,y_val = train_test_split(X_train1, y_train1, test_size=0.3, random_state=1)print('The shape of training X:',X_train.shape)print('The shape of training y:',y_train.shape)print('The shape of test X:',X_test.shape)print('The shape of test y:',y_test.shape)print('The shape of validation X:',X_val.shape)print('The shape of validation y:',y_val.shape)
设置第一层分类器
from sklearn.svm import SVCfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifierfrom sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
clfs = [SVC(probability=True),RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=5,n_jobs=-1,criterion=’gini’),KNeighborsClassifier()]
设置第二层分类器
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionlr = LinearRegression()
第一层
val_features = np.zeros((X_val.shape[0],len(clfs)))test_features = np.zeros((X_test.shape[0],len(clfs)))
for i,clf in enumerate(clfs): clf.fit(X_train,y_train) val_feature = clf.predict_proba(X_val)[:,1] test_feature = clf.predict_proba(X_test)[:,1] val_features[:,i] = val_feature test_features[:,i] = test_feature
第二层
lr.fit(val_features,y_val)
输出预测的结果
lr.fit(val_features,y_val)from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_scorecross_val_score(lr,test_features,y_test,cv=5)
到此这篇关于Python集成学习之Blending算法详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python Blending算法内容请搜索好吧啦网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦网!
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备