python 存储json数据的操作
本篇我们将学习简单的json数据的存储
首先我们需要引入json模块:import json
这里我们模拟一个常见常见,我们让用户输入用户名、密码,在密码输入完成后提示用户再次输入密码来确认自己的输入,如果两次密码一致,那么我们将用户名和密码以json格式写入文件,否则提示用户再次输入密码。
name = input('please enter your name:')password = input('please enter your password:')confirm_password = input('confirm your password:')while password != confirm_password: print('input password inconsistencies,please try again') password = input('please enter your password:') confirm_password = input('confirm your password:')
我们运行下代码确保我们的准备工作没有问题:
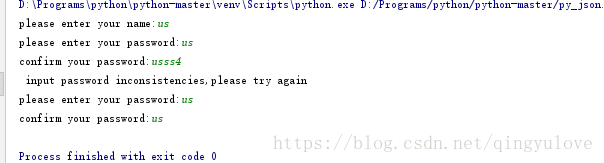
ok,我们可以通过用户输入拿到用户名和密码,接下来,我们就需要将两者以json格式存入文件了。
首先,我们将我们的输入转化为json对象:
user_info = json.dumps({’username’: name, ’password’: password}, sort_keys=True, indent=4, ensure_ascii=False)print(user_info)
这里我们使用了json.dumps函数,该函数 用于将 Python 对象编码成 JSON 字符串。
语法:
def dumps(obj, *, skipkeys=False, ensure_ascii=True, check_circular=True, allow_nan=True, cls=None, indent=None, separators=None, default=None, sort_keys=False, **kw) Inferred type: (obj: Any, Any, skipkeys: bool, ensure_ascii: bool, check_circular: bool, allow_nan: bool, cls: Any, indent: Any, separators: Any, default: Any, sort_keys: bool, kw: Dict[str, Any]) -> str
其中sort_keys是用来指定在json格式的对象里面是否按照key的名称来进行排序,indent参数则指定缩进的空格数目。
最后的输入格式如下:
{ 'password': 'us', 'username': 'us'}
那么接下来我们就将这个json对象写入到文件中去:
with open(’user_info.json’, ’w’, encoding=’utf-8’) as json_file: json.dump(user_info, json_file, ensure_ascii=False) print('write json file success!')
这里我们需要学习一个函数json.dump:
def dump(obj, fp, *, skipkeys=False, ensure_ascii=True, check_circular=True, allow_nan=True, cls=None, indent=None, separators=None, default=None, sort_keys=False, **kw) Inferred type: (obj: Any, fp: {write}, Any, skipkeys: bool, ensure_ascii: bool, check_circular: bool, allow_nan: bool, cls: Any, indent: Any, separators: Any, default: Any, sort_keys: bool, kw: Dict[str, Any]) -> None
这个函数有两个参数是我们必须要填写的:obj(我们要存储的数据), fp(文件句柄,也就是我们要存在那个文件里面)。
ensure_ascii=False这个参数是处理我们希望在json对象里面可以包含中文的场景
If ensure_ascii is false, then the strings written to fp can contain non-ASCII characters if they appear in strings contained in obj. Otherwise, all such characters are escaped in JSON strings.
如果不指定ensure_ascii=False,那么当我们的数据里面包含中文的时候:
{'username': 'zhangu4e09', 'password': 'ddd'}
会有如上的显示内容。
我们运行程序,依次输入用户名和密码:
please enter your name:usplease enter your password:usconfirm your password:us{'username': 'us', 'password': 'us'}write json file success!Process finished with exit code 0
然后我们看下文本文件中的内容:

接下来我们就需要学习一下怎么读取json格式的内容了。
with open(’user_info.json’, ’r’, encoding=’utf-8’) as json_file: data = json.load(json_file) print(data)
读取json数据需要使用json.load函数:
def load(fp, *, cls=None, object_hook=None, parse_float=None, parse_int=None, parse_constant=None, object_pairs_hook=None, **kw) Inferred type: (fp: {read}, Any, cls: Any, object_hook: Any, parse_float: Any, parse_int: Any, parse_constant: Any, object_pairs_hook: Any, kw: Dict[str, Any]) -> Any
这里我们需要提供一个参数fp,也就是我们要操作的文件句柄。
程序运行输出:
{'username': 'us', 'password': 'us'}
我们可以打印一下json.load返回的是什么类型的:
print(type(data))
输出:
<class ’str’>
可见,这是一个字符串,这是为什么呢?难道不应该返回的是python对应的对象吗?
在上面的代码中我们在写入文件前面调用过:
user_info = json.dumps({’username’: name, ’password’: password}, ensure_ascii=False)
这一行代码,大家还记得吧,它返回的是一个json字符串,所以上面的例子中我们需要使用json.loads重新反序列化为python对象,这一点大家留意一下,上面的例子我们是为了给大家演示json.loads的相关用法,使用如下:
data = json.loads(data)print(type(data))print(data[’username’])
如果没有这行代码,那么 data = json.load(json_file)返回的就是我们自己组织的数据结构了,如果还是{‘username’: name, ‘password’: password}这种格式,那么返回就是一个字典对象。
下面我们在通过一个list来看一下:
data = [1,2,3,4,5]with open(’user_info.json’, ’w’, encoding=’utf-8’) as json_file: json.dump(data, json_file, ensure_ascii=False)with open(’user_info.json’, ’r’, encoding=’utf-8’) as json_file: data = json.load(json_file) print(type(data)) print(data)
运行程序:
<class ’list’>
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
补充:Python创建并保存json文件,支持数据更新保存
大家还是直接看代码吧~import jsonclass Params(): '''Class that loads hyperparameters from a json file.Example:```params = Params(json_path)print(params.learning_rate)params.learning_rate = 0.5 # change the value of learning_rate in params```''' def __init__(self, json_path):with open(json_path) as f: params = json.load(f) # 将json格式数据转换为字典 self.__dict__.update(params) def save(self, json_path):with open(json_path, ’w’) as f: json.dump(self.__dict__, f, indent=4) # indent缩进级别进行漂亮打印 def update(self, json_path):'''Loads parameters from json file'''with open(json_path) as f: params = json.load(f) self.__dict__.update(params) @property # Python内置的@property装饰器就是负责把一个方法变成属性调用的 def dict(self):'''Gives dict-like access to Params instance by `params.dict[’learning_rate’]'''return self.__dict__if __name__ == ’__main__’: parameters = {'SEED': 1, 'dataset': 'Omniglot', 'meta_lr': 1e-3, 'num_episodes': 5000, 'num_classes': 5, 'num_samples': 1, 'num_query': 10, 'num_steps': 100, 'num_inner_tasks': 8, 'num_train_updates': 1, 'num_eval_updates': 1, 'save_summary_steps': 100, 'num_workers': 1 } json_str = json.dumps(parameters, indent=4) with open(’params.json’, ’w’) as f: # 创建一个params.json文件f.write(json_str) # 将json_str写到文件中 params = Params(’params.json’) params.SEED = 2 # 修改json中的数据 params.save(’params.json’) # 将修改后的数据保存
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦网。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教。
相关文章:
 网公网安备
网公网安备