Mybatis 实现动态组装查询条件,仿SQL模式
以前比较习惯使用Hibernate,后来觉得mybatis不能按我想要的自动组装为SQL查询条件,所以提供该工具类;
效果图:


如图所示,根据条件自动组装查询条件,下面来说一下实现方法:
1. ServiceImpl书写注意项Page<SysLogin> resultPage = null;try { PageHelper.startPage(pager.getCurrentPage(), pager.getPageSize()); // 判断是否有分页 if (ObjectHelper.isNotEmpty(pager.getDirection()) && ObjectHelper.isNotEmpty(pager.getProperties())) {specification.addOrderBy(pager.getProperties(),pager.getDirection()); } // 判断是否存在逻辑删除筛选 String sqlStr = specification.sql(); if (sqlStr.indexOf('deleted') == -1) {specification.eq('deleted', '0'); } resultPage = this.sysLoginMapper.page(specification.sql());} catch (Exception e) { result = Result.newFailure('数据错误', '在获取分页列表时发生异常。'); log.error(SimpleLogFormater.formatException(result.getMessage(), e)); return result;}2. Mapper.java 书写
查询条件非Map对象,直接就是SQL语句了;
/** * 分页查询数据 * * @return */ Page<T> page(String sqlStr);3. 关于XML的配置,会拼装SQL语句
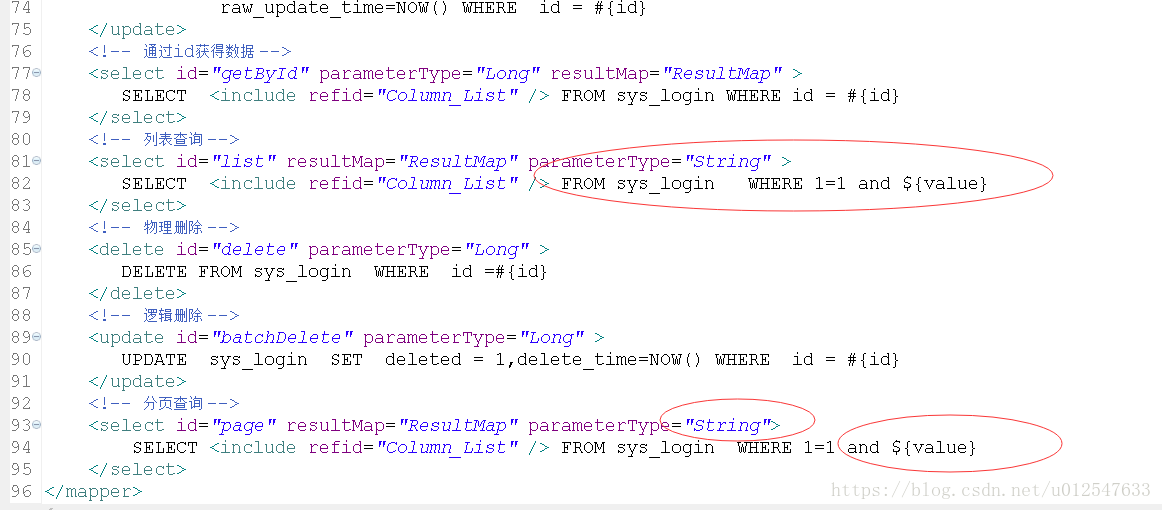
附:SQL拼装工具类
/** * @Description: (用一句话描述该文件做什么) * @author heliang * @date 2018-7-6 下午6:43:42 * @version V2.1 */package com.onem2.base.common;import com.onem2.base.helper.ObjectHelper; /** * @ClassName: Specification * @Description: (这里用一句话描述这个类的作用) * @author heliang * @date 2018-7-6 下午6:43:42 * @version V2.1 * Update Logs: * Name: * Date: * Description: 初始化 */ public class Specification { private StringBuilder where = new StringBuilder(); private String groupBy; private String having; private String orderBy; public StringBuilder getWhere() {return where; } public void setWhere(StringBuilder where) {this.where = where; } public String getGroupBy() {return groupBy; } public void setGroupBy(String groupBy) {this.groupBy = groupBy; } public String getHaving() {return having; } public void setHaving(String having) {this.having = having; } public String getOrderBy() {return orderBy; } public void setOrderBy(String orderBy) {this.orderBy = orderBy; } public Specification addOrderBy(String sort, String order) {if (!isEmpty(sort) && !isEmpty(order)) { this.orderBy = ObjectHelper.underscoreName(sort) + ' ' + order;}return this; } public Specification orLike(String value, String columns) {if (!isEmpty(value)) { StringBuffer strBuf = new StringBuffer(''); for (String column : columns.split(',')) {strBuf.append(ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' like ’%'+ value + '%’ or '); } String orLikeStr = strBuf.substring(0, strBuf.lastIndexOf('or')); where.append(' and (' + orLikeStr + ')');}return this; } public Specification eq(String column, String value) {if (!isEmpty(value)) { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' = ’' + sqlParam(value) + '’');}return this; } public Specification ne(String column, String value) {if (!isEmpty(value)) { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' != ’' + sqlParam(value) + '’');}return this; } public Specification like(String column, String value) {if (!isEmpty(value)) { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' like ’%' + sqlParam(value) + '%’');}return this; } public Specification notLike(String column, String value) {if (!isEmpty(value)) { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' not like ’%' + sqlParam(value) + '%’');}return this; } public Specification in(String column, String... values) {if (!isEmpty(values)) { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' in (' + inValuesString(values) + ')');}return this; } public Specification notIn(String column, String... values) {if (!isEmpty(values)) { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' not in (' + inValuesString(values) + ')');}return this; } public Specification gt(String column, String value) {if (!isEmpty(value)) { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' > ’' + sqlParam(value) + '’');}return this; } public Specification gte(String column, String value) {if (!isEmpty(value)) { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' >= ’' + sqlParam(value) + '’');}return this; } public Specification lt(String column, String value) {if (!isEmpty(value)) { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' < ’' + sqlParam(value) + '’');}return this; } public Specification lte(String column, String value) {if (!isEmpty(value)) { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' <= ’' + sqlParam(value) + '’');}return this; } public Specification between(String column, String from, String to) {if (isEmpty(from) && isEmpty(to)) { return this;}if (isEmpty(to)) { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' >= ’' + sqlParam(from) + '’');} else if (isEmpty(from)) { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' <= ’' + sqlParam(to) + '’');} else { where.append(' and ' + ObjectHelper.underscoreName(column) + ' between ’' + sqlParam(from) + '’ and ’' + sqlParam(to) + '’');}return this; } public String sql() {StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder('');final int a = 4;final int b = 5;if (where.length() > a) { sql.append(' ' + where.substring(b));}if (!isEmpty(groupBy)) { sql.append(' group by ' + groupBy);}if (!isEmpty(having)) { sql.append(' having ' + having);}if (!isEmpty(orderBy)) { sql.append(' order by ' + orderBy);}return sql.toString(); } public String toString() {return sql(); } private static boolean isEmpty(String value) {return value == null || ''.equals(value) || value.trim().length() == 0; } private static boolean isEmpty(String[] values) {if (values == null || values.length == 0) { return true;}for (String value : values) { if (!isEmpty(value)) {return false; }}return true; } private static String inValuesString(String[] values) {StringBuilder string = new StringBuilder();for (String value : values) { if (isEmpty(value)) {continue; } string.append(’’’); string.append(value); string.append(’’’); string.append(’,’);}if (string.length() > 0) { string.deleteCharAt(string.length() - 1);}return string.toString(); } private static String sqlParam(String sqlParam) {return sqlParam.replaceAll('([’;]+|(--)+)', ''); }}
附:ObjectHelper 工具源码:
package com.onem2.base.helper;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;import java.util.List;/** * Object帮助类 功能:此类提供处理 <Object>对象一系列方法 * * @author 贺亮 * */public class ObjectHelper { /** * 将id数组转换为id集合 * * @param ids * @return */ public static List<Long> initIds(String[] ids) {List<Long> list = new ArrayList<Long>();list.add(-1L);for (int i = 0; i < ids.length; i++) { list.add(Long.valueOf(ids[i]));}return list; } /** * 组装条件 * * @param str * @return */ public static List<String> strToList(String str) {if (isEmpty(str)) { return null;}String[] strs = str.split(',');List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();for (int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++) { list.add(strs[i]);}return list; } /** * 判断这个Object是否为Null或长度为0 * * @param obj * @return */ public static boolean isEmpty(Object obj) {if (obj == null) { return true;}if (obj instanceof Collection) { return ((Collection<?>) obj).isEmpty();} if (obj instanceof String) { return ((String) obj).equalsIgnoreCase('null') | ((String) obj).trim().toString().equals('');} if (obj instanceof StringBuffer) { return ((StringBuffer) obj).length() == 0;} if (obj.getClass().isArray()) { try {Object[] a = (Object[]) obj; boolean b = true;for (Object o : a) { b = b & isEmpty(o); if (!b) {break; }} return b; } catch (ClassCastException e) { }}return false; } /** * 判断这个Object是否不为Null或长度不为0 * * @param obj * @return */ public static boolean isNotEmpty(Object obj) {return !isEmpty(obj); } /** * 返回首字母大写单词 * * @param str * @return */ public static String lcyFirstLetterToUpper(String str) {return str.replaceFirst(str.substring(0, 1), str.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase()); } /** * 转换为下划线 * * @param camelCaseName * @return */ public static String underscoreName(String camelCaseName) {StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();if (camelCaseName != null && camelCaseName.length() > 0) { result.append(camelCaseName.substring(0, 1).toLowerCase()); for (int i = 1; i < camelCaseName.length(); i++) {char ch = camelCaseName.charAt(i);if (Character.isUpperCase(ch)) { result.append('_'); result.append(Character.toLowerCase(ch));} else { result.append(ch);} }}return result.toString(); } /** * 转换为驼峰 * * @param underscoreName * @return */ public static String camelCaseName(String underscoreName) {StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();if (underscoreName != null && underscoreName.length() > 0) { boolean flag = false; for (int i = 0; i < underscoreName.length(); i++) {char ch = underscoreName.charAt(i);if ('_'.charAt(0) == ch) { flag = true;} else { if (flag) {result.append(Character.toUpperCase(ch));flag = false; } else {result.append(ch); }} }}return result.toString(); } public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(underscoreName('loginName')); }}
这样就可以做到动态生成查询条件,复杂的查询条件也不会去改动XML配置了。
mybatis原理:参数解析与SQL动态组装过程mybatis执行sql之前, 需要经过参数解析、sql动态组装等过程,本文主要聊聊mybatis的:
(1)参数解析原理及其过程
(2)sql动态组装原理及其过程
一、数据准备1.实体类,省略了set、get方法
public class User { private String id; private String username; private String password; private Integer isValid;}
2.mapper接口UserMapper,可以看作是一个根据用户名和密码的登录接口
User getUserByUsernameAndPassword(@Param('name') String username, @Param('pwd') String password);
3.mapper映射
<select resultType='com.qxf.pojo.User'>select id,username,password,is_valid as isValid from t_user<where> <if test='name != null and name != ’’'>username = #{name} </if> <if test='pwd != null and pwd != ’’'>and password = #{pwd} </if></where> </select>
4.测试,mybatis-config.xml配置文件按一般配置即可,这里就不贴代码了
//读取配置信息InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream('mybatis-config.xml');//根据配置信息,创建SqlSession工厂SqlSessionFactory factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);//SqlSession工厂创建SqlSessionSqlSession sqlSession = factory.openSession();//获取接口的代理对象UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);//执行相应的接口方法User user = mapper.getUserByUsernameAndPassword('张三2', null);System.out.println(user);
下面将以这句代码为入口:
(注意,这里只是为了测试,给密码参数传递了null,正常情况不会这样传递参数的,不然结果返回一个List集合就会报错的)
//执行相应的接口方法User user = mapper.getUserByUsernameAndPassword('张三2', null);二、参数解析原理及其过程
首先要明白一点,返回的是mapper接口的代理对象,所以会来到MapperProxy的invoke方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try { // Object对象的方法,则直接执行 if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return method.invoke(this, args); } if (method.isDefault()) {return this.invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args); }} catch (Throwable var5) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(var5);}// 获取mapperMethod,这里面就会进行参数解析MapperMethod mapperMethod = this.cachedMapperMethod(method);// 执行方法return mapperMethod.execute(this.sqlSession, args); }
重点关注这句:
// 获取mapperMethod,这里面就会进行参数解析MapperMethod mapperMethod = this.cachedMapperMethod(method);
参数的解析可以分成两部:
(1)形参的解析
(2)实参的封装
(1)形成的解析
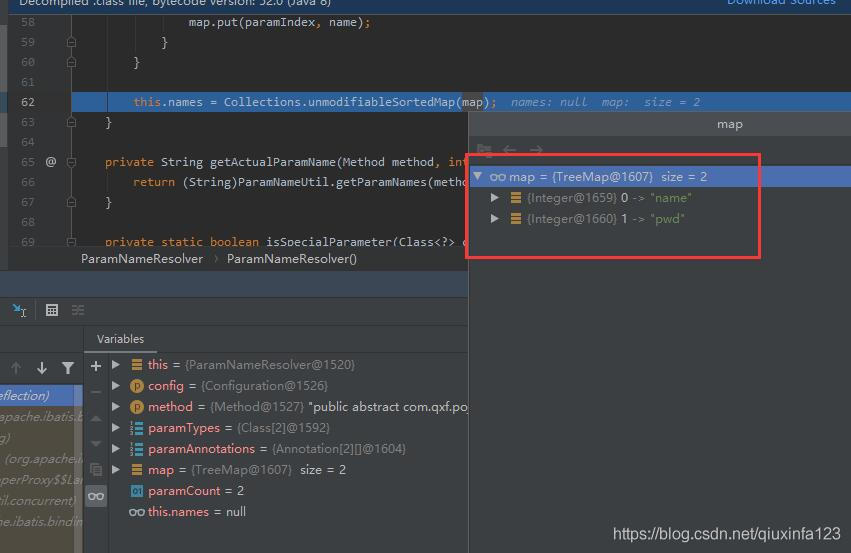
一路跟进去,最终会来到 ParamNameResolver,暂且叫做参数名称解析器吧,首先会在构造器组装参数的位置和名称的对应关系,如果我们使用了@Param注解,则会使用我们定义的名称,否则会使用arg0、arg1....依次替代,详细代码如下:
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {// 获取参数列表中,每一个参数的类型Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();// 获取参数注解,因为每个参数可能有多个注解,所以是二维数组Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();// 存放结果的mapSortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap();// 参数个数int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length; for(int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; ++paramIndex) { if (!isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {// 参数名称String name = null;// 参数的注解数组Annotation[] var9 = paramAnnotations[paramIndex];// 参数注解的个数int var10 = var9.length;// 遍历每个注解,找到Param注解,拿到value作为参数名称for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) { Annotation annotation = var9[var11]; if (annotation instanceof Param) {this.hasParamAnnotation = true;name = ((Param)annotation).value();break; }} if (name == null) { if (config.isUseActualParamName()) {name = this.getActualParamName(method, paramIndex); } if (name == null) {name = String.valueOf(map.size()); }}// 参数序号作为key,从0开始,参数名称作为值map.put(paramIndex, name); }}// 没有做什么,再一次封装而已this.names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map); }
结果是这样的:符合我们的预期的
(2)实参的封装
然后会来到getNamedParams方法对参数进一步的封装:
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {// 参数个数,这个names就是上面解析后的map,key是从0开始的参数序号,value是参数名称int paramCount = this.names.size();// 这里的args便是实参列表// 实参不为空,形参个数不为0if (args != null && paramCount != 0) { if (!this.hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {// 没有使用@Param注解,并且只有一个参数return args[(Integer)this.names.firstKey()]; } else {// 将参数封装成一个mapMap<String, Object> param = new ParamMap();int i = 0;// 对形参循环迭代for(Iterator var5 = this.names.entrySet().iterator(); var5.hasNext(); ++i) { Entry<Integer, String> entry = (Entry)var5.next(); // names中的参数名称为key,值为实参值 param.put((String)entry.getValue(), args[(Integer)entry.getKey()]); // 并添加key为param1、param2之类的通用参数 String genericParamName = 'param' + String.valueOf(i + 1); if (!this.names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {param.put(genericParamName, args[(Integer)entry.getKey()]); }} return param; }} else { return null;} }
通过源码可以发现,
(1)如果只有一个参数,并且没有使用@Param注解,就直接返回第一个参数
(2)有多个参数,则封装成一个map,key为参数参数名称,使用了@Param注解,名称就是注解中的值,否则key为arg0、arg1这种类型,同时,一定含有key为param1、param2的参数,值就是传入的值
封装后的结果如下:
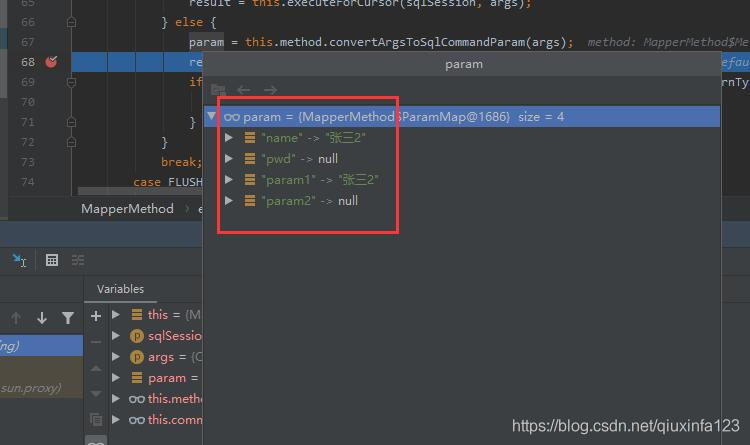
这样就完成了参数的解析过程,总结一下:
(1)解析形参,判断是否使用了@Param注解
(2)封装实参,如果只有一个,并且没有使用@Param注解,就直接返回第一个参数值,否则封装成map
三、动态组装sql原理及其过程来到CachingExecutor的如下方法,作为入口:
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {// 获取组装完成的sqlBoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);// 创建缓存keyCacheKey key = this.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);// 执行查询return this.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql); }
重点看这句:
// 获取组装完成的sqlBoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
一路跟进去,来到DynamicSqlSource的getBoundSql方法:
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {// 将参数封装成动态上下文,DynamicContext中sqlBuilder就是最后组装的sqlDynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(this.configuration, parameterObject);// 根据条件,动态组装sqlthis.rootSqlNode.apply(context);SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(this.configuration);Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();// 将#{参数}替换为?SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);Map var10000 = context.getBindings();Objects.requireNonNull(boundSql);var10000.forEach(boundSql::setAdditionalParameter);return boundSql; }
我们先看下这句:
// 根据条件,动态组装sqlthis.rootSqlNode.apply(context);
对于我们的sql:
<select resultType='com.qxf.pojo.User'>select id,username,password,is_valid as isValid from t_user<where> <if test='name != null and name != ’’'>username = #{name} </if> <if test='pwd != null and pwd != ’’'>and password = #{pwd} </if></where> </select>
每个标签都有对应的SqlNode来处理,比如if标签,就由IfSqlNode来处理,where标签,则会通过TrimSqlNode来处理,SqlNode的具体实现类如下:
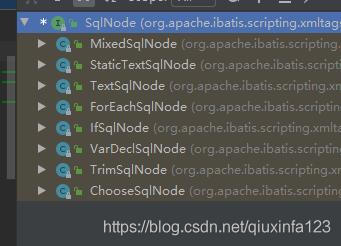
这里以IfSqlNode处理if标签为例:
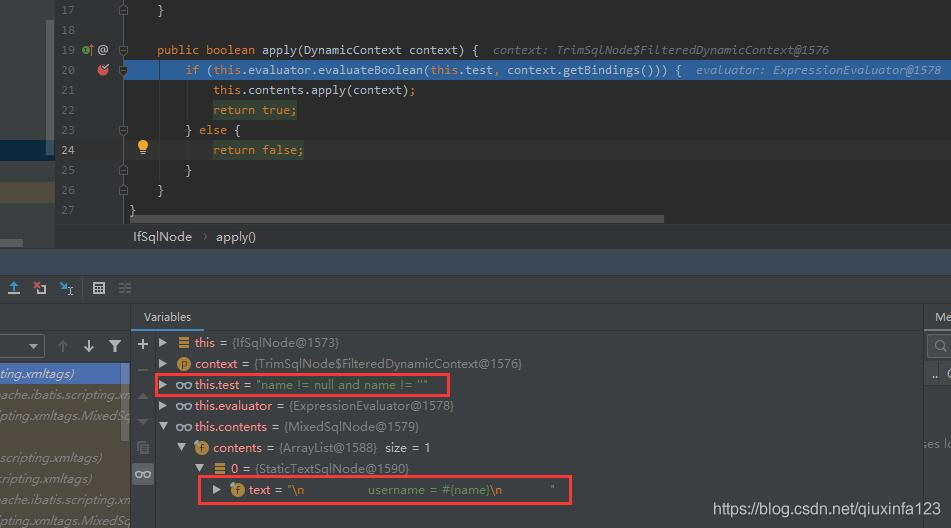
这是就是两步:
(1)判断表达式的值是否为真,这里最终使用的是Ognl来判断
(2)如果表达式的为真,就将标签内容追加到sql中去
处理结果如下:
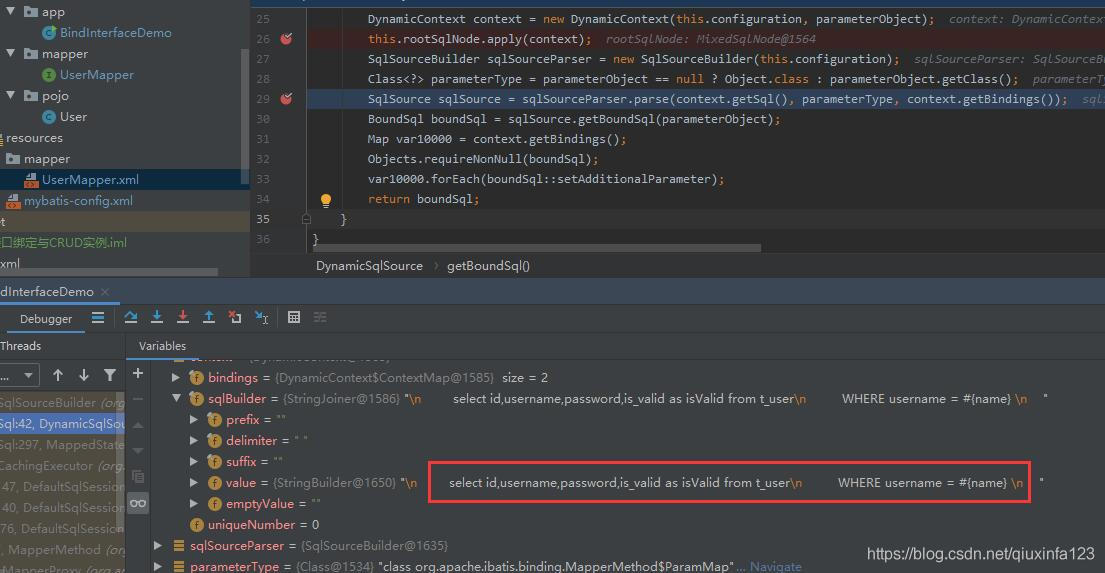
因为密码的参数传入为null,所以不会拼接密码查询条件,只拼接了用户名查询条件
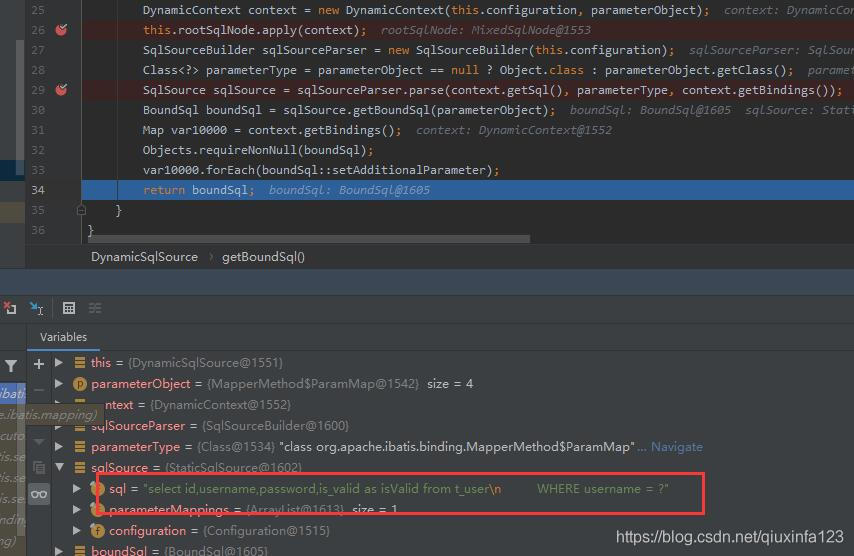
然后是将#{参数}替换为?进行占位:
// 将#{参数}替换为?SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
这个就比较简单了,可以自行看源码,最终是这样的:
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦网。
 网公网安备
网公网安备